The Evolution of Genetic Variability at the LRRK2 Locus
- PMID: 39062657
- PMCID: PMC11275506
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15070878
The Evolution of Genetic Variability at the LRRK2 Locus
Abstract
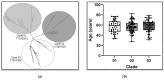
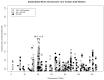
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) c.6055G>A (p.G2019S) is a frequent cause of Parkinson's disease (PD), accounting for >30% of Tunisian Arab-Berber patients. LRRK2 is widely expressed in the immune system and its kinase activity confers a survival advantage against infection in animal models. Here, we assess haplotype variability in cis and in trans of the LRRK2 c.6055G>A mutation, define the age of the pathogenic allele, explore its relationship to the age of disease onset (AOO), and provide evidence for its positive selection.
Keywords: LRRK2; Parkinson’s disease; evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
M.J.F. reports US patents associated with
Figures
References
-
- Mata I.F., Hutter C.M., González-Fernández M.C., de Pancorbo M.M., Lezcano E., Huerta C., Blazquez M., Ribacoba R., Guisasola L.M., Salvador C., et al. Lrrk2 R1441G-Related Parkinson’s Disease: Evidence of a Common Founding Event in the Seventh Century in Northern Spain. Neurogenetics. 2009;10:347–353. doi: 10.1007/s10048-009-0187-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nuytemans K., Rademakers R., Theuns J., Pals P., Engelborghs S., Pickut B., de Pooter T., Peeters K., Mattheijssens M., Van den Broeck M., et al. Founder Mutation p.R1441C in the Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 Gene in Belgian Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008;16:471–479. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201986. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Criscuolo C., De Rosa A., Guacci A., Simons E.J., Breedveld G.J., Peluso S., Volpe G., Filla A., Oostra B.A., Bonifati V., et al. The LRRK2 R1441C Mutation Is More Frequent than G2019S in Parkinson’s Disease Patients from Southern Italy. Mov. Disord. 2011;26:1733–1736. doi: 10.1002/mds.23735. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

