Mitochondrial Genome Characteristics Reveal Evolution of Acanthopsetta nadeshnyi (Jordan and Starks, 1904) and Phylogenetic Relationships
- PMID: 39062672
- PMCID: PMC11276143
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15070893
Mitochondrial Genome Characteristics Reveal Evolution of Acanthopsetta nadeshnyi (Jordan and Starks, 1904) and Phylogenetic Relationships
Abstract
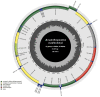
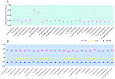
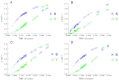
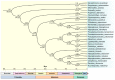
In the present study, the mitochondrial genomic characteristics of Acanthopsetta nadeshnyi have been reported and have depicted the phylogenetic relationship among Pleuronectidae. Combined with a comparative analysis of 13 PCGs, the TN93 model was used to review the neutral evolution and habitat evolution catalysis of the mitogenome to verify the distancing and purification selectivity of the mitogenome in Pleuronectidae. At the same time, a species differentiation and classification model based on mitogenome analysis data was established. This study is expected to provide a new perspective on the phylogenetic relationship and taxonomic status of A. nadeshnyi and lay a foundation for further exploration of environmental and biological evolutionary mechanisms.
Keywords: divergence time; evolutionary pressure; mitogenome; phylogenetic construction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Huang Y.K., Liu B.J., Meng F., Wang Q., Zhu K.H., Zhang J.S., Jing F., Xia L.P., Liu Y.F. The complete mitochondrial genome of Poecilia formosa (Poecilia, Cyprinodontidae) and phylogenetic studies of cyprinodontiformes. Mitochondrial DNA Part B-Resour. 2019;4:3820–3821. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1681308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lü Z.M., Zhu K.H., Jiang H., Lu X.T., Liu B.J., Ye Y.Y., Jiang L.H., Liu L.Q., Gong L. Complete mitochondrial genome of Ophichthus brevicaudatus reveals novel gene order and phylogenetic relationships of Anguilliformes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019;135:609–618. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.139. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miya M., Takeshima H., Endo H., Ishiguro N.B., Inoue J.G., Mukai T., Satoh T.P., Yamaguchi M., Kawaguchi A., Mabuchi K., et al. Major patterns of higher teleostean phylogenies: A new perspective based on 100 complete mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003;26:121–138. doi: 10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00332-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

