Genome-Wide Identification of APX Gene Family in Citrus maxima and Expression Analysis at Different Postharvest Preservation Times
- PMID: 39062690
- PMCID: PMC11276291
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15070911
Genome-Wide Identification of APX Gene Family in Citrus maxima and Expression Analysis at Different Postharvest Preservation Times
Abstract
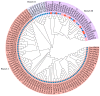
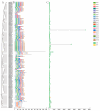
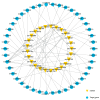
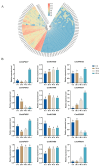
Ascorbate peroxidase (APX) is a crucial enzyme involved in cellular antioxidant defense and plays a pivotal role in modulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels under various environmental stresses in plants. This study utilized bioinformatics methods to identify and analyze the APX gene family of pomelo, while quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was employed to validate and analyze the expression of CmAPXs at different stages of fruit postharvest. This study identified 96 members of the CmAPX family in the entire pomelo genome, with uneven distribution across nine chromosomes and occurrences of gene fragment replication. The subcellular localization includes peroxisome, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. The CmAPX family exhibits a similar gene structure, predominantly consisting of two exons. An analysis of the upstream promoter regions revealed a significant presence of cis-acting elements associated with light (Box 4, G-Box), hormones (ABRE, TCA-element), and stress-related (MBS, LTR, ARE) responses. Phylogenetic and collinearity analyses revealed that the CmAPX gene family can be classified into three subclasses, with seven collinear gene pairs. Furthermore, CmAPXs are closely related to citrus, pomelo, and lemon, followed by Arabidopsis, and exhibit low homology with rice. Additionally, the transcriptomic heat map and qPCR results revealed that the expression levels of CmAPX57, CmAPX34, CmAPX50, CmAPX4, CmAPX5, and CmAPX81 were positively correlated with granulation degree, indicating the activation of the endogenous stress resistance system in pomelo cells by these genes, thereby conferring resistance to ROS. This finding is consistent with the results of GO enrichment analysis. Furthermore, 38 miRNAs were identified as potential regulators targeting the CmAPX family for post-transcriptional regulation. Thus, this study has preliminarily characterized members of the APX gene family in pomelo and provided valuable insights for further research on their antioxidant function and molecular mechanism.
Keywords: APX gene family; Citrus maxima; ascorbic acid; postharvest preservation; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Aleem M., Aleem S., Sharif I., Aleem M., Shahzad R., Khan M.I., Batool A., Sarwar G., Farooq J., Iqbal A., et al. Whole-Genome Identification of APX and CAT Gene Families in Cultivated and Wild Soybeans and Their Regulatory Function in Plant Development and Stress Response. Antioxidants. 2022;11:1626. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081626. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jardim-Messeder D., Caverzan A., Bastos G.A., Galhego V., Souza-Vieira Y., Lazzarotto F., Felix-Mendes E., Lavaquial L., Nicomedes Junior J., Margis-Pinheiro M., et al. Genome-wide, evolutionary, and functional analyses of ascorbate peroxidase (APX) family in Poaceae species. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2022;46((Suppl. S1)):e20220153. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-gmb-2022-0153. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hossain M.A., Bhattacharjee S., Armin S.M., Qian P., Xin W., Li H.Y., Burritt D.J., Fujita M., Tran L.S. Hydrogen peroxide priming modulates abiotic oxidative stress tolerance: Insights from ROS detoxification and scavenging. Front. Plant Sci. 2015;6:420. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00420. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hasanuzzaman M., Bhuyan M.H.M.B., Zulfiqar F., Raza A., Mohsin S.M., Mahmud J.A., Fujita M., Fotopoulos V. Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Defense in Plants under Abiotic Stress: Revisiting the Crucial Role of a Universal Defense Regulator. Antioxidants. 2020;9:681. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080681. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

