The Role of Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M3 in Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 39062802
- PMCID: PMC11277046
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25147560
The Role of Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M3 in Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
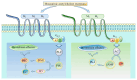
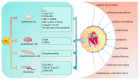
The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 (M3-mAChR) is involved in various physiological and pathological processes. Owing to specific cardioprotective effects, M3-mAChR is an ideal diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Growing evidence has linked M3-mAChR to the development of multiple CVDs, in which it plays a role in cardiac protection such as anti-arrhythmia, anti-hypertrophy, and anti-fibrosis. This review summarizes M3-mAChR's expression patterns, functions, and underlying mechanisms of action in CVDs, especially in ischemia/reperfusion injury, cardiac hypertrophy, and heart failure, opening up a new research direction for the treatment of CVDs.
Keywords: cardiomyocyte; cardiovascular diseases; endothelial cell; fibroblast; muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang S., Jiang Y., Chen J., Dai C., Liu D., Pan W., Wang L., Fasae M.B., Sun L., Wang L., et al. Activation of M3 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors Delayed Cardiac Aging by Inhibiting the Caspase-1/IL-1beta Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018;49:1208–1216. doi: 10.1159/000493332. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yue P., Zhang Y., Du Z., Xiao J., Pan Z., Wang N., Yu H., Ma W., Qin H., Wang W.H., et al. Ischemia impairs the association between connexin 43 and M3 subtype of acetylcholine muscarinic receptor (M3-mAChR) in ventricular myocytes. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2006;17:129–136. doi: 10.1159/000092074. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

