SGLT2 Inhibitors Empagliflozin and Canagliflozin Ameliorate Allergic Asthma Responses in Mice
- PMID: 39062810
- PMCID: PMC11277224
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25147567
SGLT2 Inhibitors Empagliflozin and Canagliflozin Ameliorate Allergic Asthma Responses in Mice
Abstract
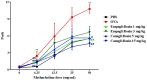
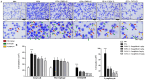
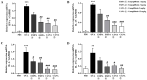
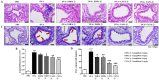
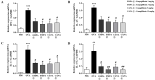
Inhibitors of sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2), such as empagliflozin and canagliflozin, have been widely used to block glucose reabsorption in the proximal tubules of kidneys in patients with diabetes. A meta-analysis suggested that SGLT2 inhibitors are associated with a decreased risk of asthma development. Therefore, we investigated whether SGLT2 inhibitors could suppress allergic asthma. Empagliflozin and canagliflozin suppressed the in vitro degranulation reaction induced by antigens in a concentration-dependent manner in RBL-2H3 mast cells. Empagliflozin and canagliflozin were administered to BALB/c mice sensitized to ovalbumin (OVA). The administration of empagliflozin or canagliflozin significantly suppressed OVA-induced airway hyper-responsiveness and increased the number of immune cells and pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNA expression levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. The administration of empagliflozin and canagliflozin also suppressed OVA-induced histopathological changes in the lungs. Empagliflozin and canagliflozin also suppressed serum IgE levels. These results suggested that empagliflozin and canagliflozin may be applicable for the treatment of allergic asthma by suppressing immune responses.
Keywords: SGLT2; allergy; asthma; canagliflozin; pulmonary pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

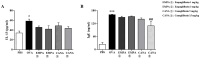
References
-
- Boulet L.P., Boulay M., Côté A., FitzGerald J.M., Bergeron C., Lemière C., Lougheed M.D., Vandemheen K.L., Aaron S.D. Airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in subjects with respiratory symptoms and normal spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2023;61:2201194. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01194-2022. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

