Metabolic Crosstalk between Liver and Brain: From Diseases to Mechanisms
- PMID: 39062868
- PMCID: PMC11277155
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25147621
Metabolic Crosstalk between Liver and Brain: From Diseases to Mechanisms
Abstract
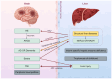
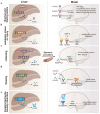
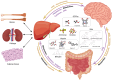
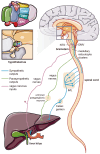
Multiple organs and tissues coordinate to respond to dietary and environmental challenges. It is interorgan crosstalk that contributes to systemic metabolic homeostasis. The liver and brain, as key metabolic organs, have their unique dialogue to transmit metabolic messages. The interconnected pathogenesis of liver and brain is implicated in numerous metabolic and neurodegenerative disorders. Recent insights have positioned the liver not only as a central metabolic hub but also as an endocrine organ, capable of secreting hepatokines that transmit metabolic signals throughout the body via the bloodstream. Metabolites from the liver or gut microbiota also facilitate a complex dialogue between liver and brain. In parallel to humoral factors, the neural pathways, particularly the hypothalamic nuclei and autonomic nervous system, are pivotal in modulating the bilateral metabolic interplay between the cerebral and hepatic compartments. The term "liver-brain axis" vividly portrays this interaction. At the end of this review, we summarize cutting-edge technical advancements that have enabled the observation and manipulation of these signals, including genetic engineering, molecular tracing, and delivery technologies. These innovations are paving the way for a deeper understanding of the liver-brain axis and its role in metabolic homeostasis.
Keywords: autonomic nervous system; brain; hepatokines; interorgan crosstalk; liver; metabolism; metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Castera L., Laouenan C., Vallet-Pichard A., Vidal-Trécan T., Manchon P., Paradis V., Roulot D., Gault N., Boitard C., Terris B., et al. High Prevalence of NASH and Advanced Fibrosis in Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Study of 330 Outpatients Undergoing Liver Biopsies for Elevated ALT, Using a Low Threshold. Diabetes Care. 2023;46:1354–1362. doi: 10.2337/dc22-2048. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lazarus J.V., Mark H.E., Villota-Rivas M., Palayew A., Carrieri P., Colombo M., Ekstedt M., Esmat G., George J., Marchesini G., et al. The Global NAFLD Policy Review and Preparedness Index: Are Countries Ready to Address This Silent Public Health Challenge? J. Hepatol. 2022;76:771–780. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.10.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cunnane S.C., Trushina E., Morland C., Prigione A., Casadesus G., Andrews Z.B., Beal M.F., Bergersen L.H., Brinton R.D., de la Monte S., et al. Brain Energy Rescue: An Emerging Therapeutic Concept for Neurodegenerative Disorders of Ageing. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020;19:609–633. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0072-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen J.V., Christensen S.K., Westi E.W., Diaz-delCastillo M., Tanila H., Schousboe A., Aldana B.I., Waagepetersen H.S. Deficient Astrocyte Metabolism Impairs Glutamine Synthesis and Neurotransmitter Homeostasis in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021;148:105198. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105198. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

