Genome-Wide Association Studies on Resistance to Pea Weevil: Identification of Novel Sources of Resistance and Associated Markers
- PMID: 39063162
- PMCID: PMC11276686
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25147920
Genome-Wide Association Studies on Resistance to Pea Weevil: Identification of Novel Sources of Resistance and Associated Markers
Abstract
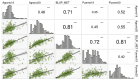
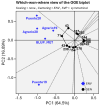
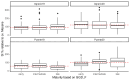
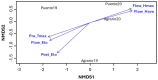
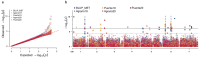
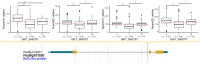
Little resistance to the pea weevil insect pest (Bruchus pisorum) is available in pea (Pisum sativum) cultivars, highlighting the need to search for sources of resistance in Pisum germplasm and to decipher the genetic basis of resistance. To address this need, we screened the response to pea weevil in a Pisum germplasm collection (324 accession, previously genotyped) under field conditions over four environments. Significant variation for weevil seed infestation (SI) was identified, with resistance being frequent in P. fulvum, followed by P. sativum ssp. elatius, P. abyssinicum, and P. sativum ssp. humile. SI tended to be higher in accessions with lighter seed color. SI was also affected by environmental factors, being favored by high humidity during flowering and hampered by warm winter temperatures and high evapotranspiration during and after flowering. Merging the phenotypic and genotypic data allowed genome-wide association studies (GWAS) yielding 73 markers significantly associated with SI. Through the GWAS models, 23 candidate genes were found associated with weevil resistance, highlighting the interest of five genes located on chromosome 6. These included gene 127136761 encoding squalene epoxidase; gene 127091639 encoding a transcription factor MYB SRM1; gene 127097033 encoding a 60S ribosomal protein L14; gene 127092211, encoding a BolA-like family protein, which, interestingly, was located within QTL BpLD.I, earlier described as conferring resistance to weevil in pea; and gene 127096593 encoding a methyltransferase. These associated genes offer valuable potential for developing pea varieties resistant to Bruchus spp. and efficient utilization of genomic resources through marker-assisted selection (MAS).
Keywords: Bruchus; GWAS; Pisum; resistance breeding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of quantitative trait loci (QTL) controlling resistance to pea weevil (Bruchus pisorum) in a high-density integrated DArTseq SNP-based genetic map of pea.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 8;10(1):33. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56987-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31913335 Free PMC article.
-
Pea weevil damage and chemical characteristics of pea cultivars determining their resistance to Bruchus pisorum L.Bull Entomol Res. 2016 Apr;106(2):268-77. doi: 10.1017/S0007485315001133. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Bull Entomol Res. 2016. PMID: 26837535
-
Genome-wide association mapping of partial resistance to Aphanomyces euteiches in pea.BMC Genomics. 2016 Feb 20;17:124. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2429-4. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26897486 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on the genetic improvement of health- and nutrition-related traits in pea.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021 Jan;158:353-362. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.11.020. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33250319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovations in functional genomics and molecular breeding of pea: exploring advances and opportunities.aBIOTECH. 2024 Jan 30;5(1):71-93. doi: 10.1007/s42994-023-00129-1. eCollection 2024 Mar. aBIOTECH. 2024. PMID: 38576433 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rubiales D., Mikic A. Introduction: Legumes in Sustainable Agriculture. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2014;34:2–3. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2014.897896. - DOI
-
- Teshome A., Mendesil E., Geleta M., Andargie D., Anderson P., Rämert B., Seyoum E., Hillbur Y., Dagne K., Bryngelsson T. Screening the primary gene pool of field pea (Pisum sativum L. subsp. sativum) in Ethiopia for resistance against pea weevil (Bruchus pisorum L.) Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2015;62:525–538. doi: 10.1007/s10722-014-0178-2. - DOI
-
- Clement S.L., McPhee K.E., Elberson L.R., Evans M.A. Pea weevil, Bruchus pisorum L. (Coleoptera: Bruchidae), resistance in Pisum sativum × Pisum fulvum interspecific crosses. Plant Breed. 2009;128:478–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0523.2008.01603.x. - DOI
-
- Mishra S.K., Macedo M.L.R., Panda S.K., Panigrahi J. Bruchid pest management in pulses: Past practices, present status and use of modern breeding tools for development of resistant varieties. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2018;172:4–19. doi: 10.1111/aab.12401. - DOI
-
- Reddy G.V.P., Sharma A., Gadi R.L. Biology, Ecology, and Management of the Pea Weevil (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2018;111:161–171. doi: 10.1093/aesa/sax078. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

