Vasorelaxant and Hypotensive Effects of Galla chinensis in Rats
- PMID: 39063203
- PMCID: PMC11276969
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25147962
Vasorelaxant and Hypotensive Effects of Galla chinensis in Rats
Abstract
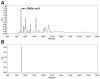
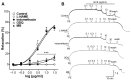
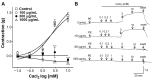
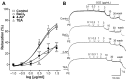
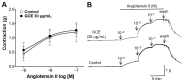
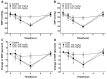
Previous studies have revealed the medicinal and therapeutic effects of Galla chinensis. However, no studies have focused on the antihypertensive effects of G. chinensis. Therefore, we aimed to determine the vasorelaxant and hypotensive effects of G. chinensis 50% ethanolic extract (GCE). To evaluate the vascular relaxing effect of GCE, experiments were conducted using aortic segments dissected from Sprague Dawley rats. GCE showed a vasorelaxant effect via the nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate pathway, inhibiting Ca2+ channels, and activating K+ channels. The hypotensive effects of GCE were evaluated in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). The SHRs were randomly divided into a control group and orally administered GCE group (100 or 300 mg/kg). The systolic and diastolic blood pressure decreased significantly by -19.47 ± 4.58% and -31.14 ± 7.66% in the GCE 100 mg/kg group, and -21.64 ± 2.40% and -31.91 ± 5.75% in the GCE 300 mg/kg group at 4 h after administration. Considering its vasorelaxant and hypotensive effects, our results indicate that GCE may be a valuable solution for the control of hypertension. However, further studies on the long-term administration and toxicity of GCE are required.
Keywords: Chinese gallnut; Galla chinensis; NO/cGMP pathway; blood pressure; cardiovascular diseases; endothelium; hypertension; hypotensive effect; spontaneously hypertensive rat; vasorelaxant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dunbar S.B., Khavjou O.A., Bakas T., Hunt G., Kirch R.A., Leib A.R., Morrison R.S., Poehler D.C., Roger V.L., Whitsel L.P., et al. Projected Costs of Informal Caregiving for Cardiovascular Disease: 2015 to 2035 A Policy Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:E558–E577. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000570. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

