Recent Advances in Efficient Lutein-Loaded Zein-Based Solid Nano-Delivery Systems: Establishment, Structural Characterization, and Functional Properties
- PMID: 39063387
- PMCID: PMC11276201
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13142304
Recent Advances in Efficient Lutein-Loaded Zein-Based Solid Nano-Delivery Systems: Establishment, Structural Characterization, and Functional Properties
Abstract
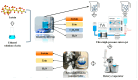
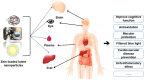
Plant proteins have gained significant attention over animal proteins due to their low carbon footprint, balanced nutrition, and high sustainability. These attributes make plant protein nanocarriers promising for applications in drug delivery, nutraceuticals, functional foods, and other areas. Zein, a major by-product of corn starch processing, is inexpensive and widely available. Its unique self-assembly characteristics have led to its extensive use in various food and drug systems. Zein's functional tunability allows for excellent performance in loading and transporting bioactive substances. Lutein offers numerous bioactive functions, such as antioxidant and vision protection, but suffers from poor chemical stability and low bioavailability. Nano-embedding technology can construct various zein-loaded lutein nanodelivery systems to address these issues. This review provides an overview of recent advances in the construction of zein-loaded lutein nanosystems. It discusses the fundamental properties of these systems; systematically introduces preparation techniques, structural characterization, and functional properties; and analyzes and predicts the target-controlled release and bioaccessibility of zein-loaded lutein nanosystems. The interactions and synergistic effects between Zein and lutein in the nanocomplexes are examined to elucidate the formation mechanism and conformational relationship of zein-lutein nanoparticles. The physical and chemical properties of Zein are closely related to the molecular structure. Zein and its modified products can encapsulate and protect lutein through various methods, creating more stable and efficient zein-loaded lutein nanosystems. Additionally, embedding lutein in Zein and its derivatives enhances lutein's digestive stability, solubility, antioxidant properties, and overall bioavailability.
Keywords: functional properties; lutein; nano-delivery system; structural characterization; zein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fabrication and Characterization of Lutein-Loaded Nanoparticles Based on Zein and Sophorolipid: Enhancement of Water Solubility, Stability, and Bioaccessibility.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Oct 30;67(43):11977-11985. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05175. Epub 2019 Oct 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 31589424
-
Lutein encapsulation into dual-layered starch/zein gels using 3D food printing: Improved storage stability and in vitro bioaccessibility.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;266(Pt 2):131305. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131305. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38569990
-
Zein-derived peptides as nanocarriers to increase the water solubility and stability of lutein.Food Funct. 2018 Jan 24;9(1):117-123. doi: 10.1039/c7fo01652b. Food Funct. 2018. PMID: 29336438
-
Nanoencapsulation and delivery of bioactive ingredients using zein nanocarriers: approaches, characterization, applications, and perspectives.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 10;33(5):1037-1057. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01489-6. eCollection 2024 Apr. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38440671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research advances in Zein-based nano-delivery systems.Front Nutr. 2024 May 9;11:1379982. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1379982. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38798768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ma Y.Q., You T.T., Wang J., Jiang Y., Niu J.C. Research progress on construction of lutein-loaded nano delivery system and their improvements on the bioactivity. Coatings. 2022;12:1449. doi: 10.3390/coatings12101449. - DOI
-
- Lu C.C., Yen G.C. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activity of functional foods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015;2:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2014.11.002. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- No. LH2023C116/Heilongjiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. YSTSXK202204/Heilongjiang Provincial Foundation for the Characteristic Discipline of Processing Technology of Plant Foods
- SJGY20220404/Heilongjiang Province Higher Education Teaching Reform Project
- GJQTYB202124/Qiqihar University Educational Science Research Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

