Bidirectional Association between Periodontitis and Thyroid Disease: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 39063437
- PMCID: PMC11277102
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph21070860
Bidirectional Association between Periodontitis and Thyroid Disease: A Scoping Review
Abstract
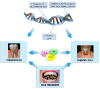
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. Due to the development of chronic inflammation, periodontitis can contribute to the development of several systemic diseases, including thyroid disease. Thyroid pathology includes benign, malignant, and autoimmune conditions leading to hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or euthyroidism. Alterations in thyroid hormones, especially hypothyroidism, can reveal significant oral manifestations, including periodontitis. This scoping review aims to explore the probable causal relationship between periodontitis and thyroid disease, in terms of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. The search strategy follows the PRISMA-ScR guidelines. PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane were searched from January 2014 to January 2024, entering the MESH terms "periodontitis" and "thyroid". Of 153 initial records, 20 articles were selected and discussed. There is a high prevalence of periodontitis among patients with thyroid disease, including thyroid cancer. The causes at the basis of this association are genetic factors, the oral microbiome, and proinflammatory cytokines. Periodontal treatment, specifically scaling and root planning, can ameliorate thyroid parameters. Although there are a few randomized controlled studies in the literature, this review lays the foundation for a bidirectional relationship between periodontitis and thyroid disease, the link to which is, once again, systemic inflammation.
Keywords: cytokines; hyperthyroidism; hypothyroidism; oral microbiome; periodontitis; scaling and root planning; thyroid cancer; thyroid disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

