Algorithm-Based Modular Psychotherapy Alleviates Brain Inflammation in Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- PMID: 39063640
- PMCID: PMC11278507
- DOI: 10.3390/life14070887
Algorithm-Based Modular Psychotherapy Alleviates Brain Inflammation in Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Abstract
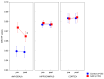
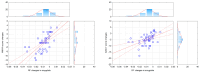
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is marked by prolonged and excessive worry, physical signs of anxiety, and associated neuroinflammation. Traditional treatments, like pharmacotherapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), often leave residual symptoms and have high relapse rates. This study aimed to explore the efficacy of algorithm-based modular psychotherapy (MoBa), a combination of CBT and mindfulness meditation as validated by the research domain criteria (RDoC), in reducing anxiety and neuroinflammation in GAD. A longitudinal design was used, with 50 patients with GAD undergoing a 12-week MoBa treatment. The patients were investigated pre- and post-treatment using MRI to measure neuroinflammatory markers (DBSI-RF, diffusion-basis spectral imaging-based restricted fraction) in the hippocampus, amygdala, and neocortex. Clinical symptoms were assessed using the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7). Results indicated significant reductions in both anxiety symptoms and MRI RF values in the amygdala, suggesting decreased neuroinflammation. A reduction in anxiety was associated with the amelioration of neuroinflammation in the amygdala. These results suggest that MoBa is effective in alleviating both the psychological and neuroinflammatory aspects of GAD, offering a promising personalized treatment approach. Future research should focus on long-term effects and the mechanisms through which MoBa impacts neuroinflammation and anxiety.
Keywords: amygdala; cognitive–behavioral therapy; generalized anxiety disorder; modular psychotherapy; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Association A.P. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
-
- Kessler R.C., Avenevoli S., Costello J., Green J.G., Gruber M.J., McLaughlin K.A., Petukhova M., Sampson N.A., Zaslavsky A.M., Merikangas K.R. Severity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication Adolescent Supplement. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2012;69:381–389. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1603. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wittchen H.U., Hoyer J. Generalized anxiety disorder: Nature and course. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2001;62((Suppl. 11)):15–19, discussion 20–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

