Understanding Galectin-3's Role in Diastolic Dysfunction: A Contemporary Perspective
- PMID: 39063659
- PMCID: PMC11277993
- DOI: 10.3390/life14070906
Understanding Galectin-3's Role in Diastolic Dysfunction: A Contemporary Perspective
Abstract
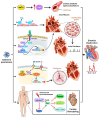
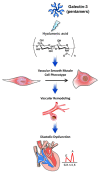
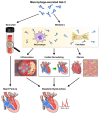
Diastolic dysfunction, a prevalent condition characterized by impaired relaxation and filling of the left ventricle, significantly contributes to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Galectin-3, a β-galactoside-binding lectin, has garnered attention as a potential biomarker and mediator of fibrosis and inflammation in cardiovascular diseases. This comprehensive review investigates the impact of galectin-3 on diastolic dysfunction. We explore its molecular mechanisms, including its involvement in cellular signaling pathways and interaction with components of the extracellular matrix. Evidence from both animal models and clinical studies elucidates galectin-3's role in cardiac remodeling, inflammation, and fibrosis, shedding light on the underlying pathophysiology of diastolic dysfunction. Additionally, we examine the diagnostic and therapeutic implications of galectin-3 in diastolic dysfunction, emphasizing its potential as both a biomarker and a therapeutic target. This review underscores the significance of comprehending galectin-3's role in diastolic dysfunction and its promise in enhancing diagnosis and treatment approaches for HFpEF patients.
Keywords: biomarker; cardiac remodeling; diastolic dysfunction; fibrosis; galectin-3; heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Simmonds S.J., Grootaert M.O.J., Cuijpers I., Carai P., Geuens N., Herwig M., Baatsen P., Hamdani N., Luttun A., Heymans S., et al. Pericyte loss initiates microvascular dysfunction in the development of diastolic dysfunction. Eur. Heart J. Open. 2024;4:oead129. doi: 10.1093/ehjopen/oead129. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Janssens J.V., Raaijmakers A.J.A., Weeks K.L., Bell J.R., Mellor K.M., Curl C.L., Delbridge L.M.D. The cardiomyocyte origins of diastolic dysfunction: Cellular components of myocardial “stiffness”. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2024;326:H584–H598. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00334.2023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aldujeli A., Tsai T.Y., Haq A., Tatarunas V., Knokneris A., Briedis K., Unikas R., Onuma Y., Brilakis E.S., Serruys P.W. Impact of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction on Functional Left Ventricular Remodeling and Diastolic Dysfunction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024;13:e033596. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.033596. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

