The Role of Pro-Inflammatory Chemokines CCL-1, 2, 4, and 5 in the Etiopathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Subjects from the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: Correlation with Different Degrees of Obesity
- PMID: 39063997
- PMCID: PMC11277753
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14070743
The Role of Pro-Inflammatory Chemokines CCL-1, 2, 4, and 5 in the Etiopathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Subjects from the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: Correlation with Different Degrees of Obesity
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is becoming a major global health concern, especially in developing nations. The high prevalence of obesity and related diabetes cases are attributed to rapid economic progress, physical inactivity, the consumption of high-calorie foods, and changing lifestyles.
Objectives: We investigated the roles of pro-inflammatory chemokines CCL1, 2, 4, and 5 in T2DM with varying levels of obesity in the Asir region of Saudi Arabia.
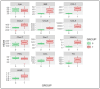
Materials and methods: In total, 170 confirmed T2DM subjects and a normal control group were enrolled. Demographic data, serum levels of CCL-1, 2, 4, and 5, and biochemical indices were assessed in the subjects and control groups by standard procedures.
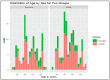
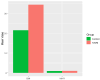
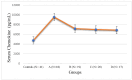
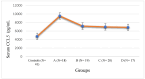
Results: T2DM subjects were divided into four groups: A (normal body weight), B (overweight), C (obese), and D (highly obese). We observed that male and female control subjects had similar mean serum concentrations of pro-inflammatory chemokines CCL-1, 2, 4, and 5. T2DM subjects in all the four groups showed significantly higher levels of all the four chemokines compared to the controls, regardless of gender. In T2DM subjects with obesity and severe obesity, the rise was most significant. There was a progressive rise in the concentrations of CCL-1, 2, and 4 in T2DM subjects with increasing BMI. Serum CCL5 levels increased significantly in all T2DM subject groups. The increase in CCL5 was more predominant in normal-weight people, compared to overweight and obese T2DM subjects.
Conclusions: Male and female control subjects had similar serum levels of pro-inflammatory chemokines CCL-1, 2, 4, and 5. The progressive rise in blood concentrations of three pro-inflammatory chemokines CCL-1, 2, and 4 in T2DM subjects with increasing BMI supports the idea that dyslipidemia and obesity contribute to chronic inflammation and insulin resistance. Serum CCL5 levels increased significantly in all T2DM subject groups. The selective and more pronounced increase in CCL5 in the T2DM group with normal BMI, compared to subjects with varying degrees of obesity, was rather surprising. Further research is needed to determine if CCL5 underexpression in overweight and obese T2DM subjects is due to some unexplained counterbalancing processes.
Keywords: CCL1; CCL2; CCL4; CCL5; obesity; pro-inflammatory chemokines; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C., Mbanya J.C., et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mir M.M., Mir R., Alghamdi M.A.A., Wani J.I., Sabah Z.U., Jeelani M., Marakala V., Sohail S.K., O’haj M., Alharthi M.H., et al. Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study. J. Pers. Med. 2022;12:735. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mir M.M., Mir R., Alghamdi M.A.A., Wani J.I., Elfaki I., Sabah Z.U., Alhujaily M., Jeelani M., Marakala V., Alharthi M.H., et al. Potential impact of GCK, MIR-196A-2 and MIR-423 gene abnormalities on the development and progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asir and Tabuk regions of Saudi Arabia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022;25:162. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12675. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

