Plasma FGF21 Concentration in Kidney Transplant Patients-Results from Prospective and Cross-Sectional Studies
- PMID: 39064306
- PMCID: PMC11278288
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13144266
Plasma FGF21 Concentration in Kidney Transplant Patients-Results from Prospective and Cross-Sectional Studies
Abstract
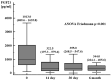
Background/Objectives: Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a protein hormone involved in physiological conditions in the regulation of energy expenditure and several metabolic processes. The aim of this present study was to analyze the effect of successful kidney transplantations on the plasma FGF21 concentration and to study the factors which may influence plasma FGF21 concentration in patients in long time after kidney transplantation. Methods: This study consisted of two independent parts. The first part was a prospective observation of CKD patients in stage 5 before and then on the 14th and 30th day and 6 months after kidney transplantation. The second part of this study was the cross-sectional study completed in patients at least one year after kidney transplantation and the control group. In CKD patients directly before and during the early period after KTx, plasma FGF21 concentrations were measured four times (immediately before and 14 and 30 days and 6 months after KTx). In patients long time after kidney transplantation and in healthy subjects, plasma FGF21 concentration was measured once. Results: Forty patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) who were either directly before or within the early period after kidney transplantation (KTx), 184 patients longtime after KTx and 50 healthy subjects were enrolled into this study. In CKD patients at the stage directly before receiving a KTx, the mean plasma FGF21 concentration was significantly higher than in the healthy subjects [1013.0 pg/mL versus 239.5 pg/mL, p < 0.001]. At 14, 30 days, and 6 months after the KTx, a significant decrease of plasma FGF21 was observed, with values of 322.5 pg/mL; 355.0 pg/mL; and 344.0 pg/mL (p < 0.001), respectively]. In patients long time after KTx, a negative correlation was found between the plasma FGF21 concentration and the estimated glomerular filtration rate and a positive correlation was found between the plasma FGF21 concentration and the BMI, the serum concentration of triglycerides, insulin, interleukin-6, CRP, and cystatin C. Conclusions: The plasma FGF21 concentration in patients with end-stage renal disease is higher than in healthy subjects and significantly decreases after a successful KTx. The plasma FGF21 concentration measured by ELISA in patients long time after kidney transplantation seems to be related to the degree of kidney function impairment and their metabolic status. The kidneys appear to be one of the main organs involved in the biodegradation and/or elimination of FGF21.
Keywords: FGF21; chronic kidney disease; fibroblast growth factor; kidney transplantation; metabolic disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma adiponectin concentration in patients after successful kidney transplantation--a single-center, observational study.Clin Nephrol. 2007 Jun;67(6):381-90. doi: 10.5414/cnp67381. Clin Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17598374
-
Circulating FGF21 levels are progressively increased from the early to end stages of chronic kidney diseases and are associated with renal function in Chinese.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 15;6(4):e18398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018398. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21525989 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Increased Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Growth Factors 19 and 21.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2019;44(5):1207-1218. doi: 10.1159/000502647. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2019. PMID: 31614355
-
Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral Bone Disease Biomarkers in Kidney Transplant Patients.Curr Med Chem. 2022 Aug 15;29(31):5230-5253. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220318105856. Curr Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35306980 Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 in chronic kidney disease.J Nephrol. 2019 Jun;32(3):365-377. doi: 10.1007/s40620-018-0550-y. Epub 2018 Nov 14. J Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30430412 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Niemczyk S., Niemczyk L., Romejko-Ciepielewska K. Basic endocrinological disorders in chronic renal failure. Endokrynol. Pol. 2012;63:250–257. - PubMed
-
- Niemczyk S., Niemczyk L., Romejko-Ciepielewska K. Adipocytokines and sex hormone disorders in patients with chronic renal failure (CRF) Endokrynol. Pol. 2012;63:148–155. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

