Advances in Microfluidic Systems and Numerical Modeling in Biomedical Applications: A Review
- PMID: 39064385
- PMCID: PMC11279158
- DOI: 10.3390/mi15070873
Advances in Microfluidic Systems and Numerical Modeling in Biomedical Applications: A Review
Abstract
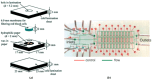
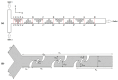
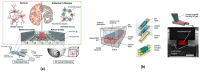
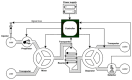
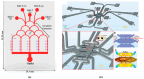
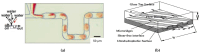
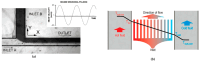
The evolution in the biomedical engineering field boosts innovative technologies, with microfluidic systems standing out as transformative tools in disease diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring. Numerical simulation has emerged as a tool of increasing importance for better understanding and predicting fluid-flow behavior in microscale devices. This review explores fabrication techniques and common materials of microfluidic devices, focusing on soft lithography and additive manufacturing. Microfluidic systems applications, including nucleic acid amplification and protein synthesis, as well as point-of-care diagnostics, DNA analysis, cell cultures, and organ-on-a-chip models (e.g., lung-, brain-, liver-, and tumor-on-a-chip), are discussed. Recent studies have applied computational tools such as ANSYS Fluent 2024 software to numerically simulate the flow behavior. Outside of the study cases, this work reports fundamental aspects of microfluidic simulations, including fluid flow, mass transport, mixing, and diffusion, and highlights the emergent field of organ-on-a-chip simulations. Additionally, it takes into account the application of geometries to improve the mixing of samples, as well as surface wettability modification. In conclusion, the present review summarizes the most relevant contributions of microfluidic systems and their numerical modeling to biomedical engineering.
Keywords: microfluidics; microfluidics systems; mixing; numerical simulation; organ-on-a-chip.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomedical Applications of Microfluidic Devices: A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;12(11):1023. doi: 10.3390/bios12111023. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Numerical evaluation and experimental validation of fluid flow behavior within an organ-on-a-chip model.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024 Jan;243:107883. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107883. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024. PMID: 37944399
-
Optimization of Microfluidics for Point-of-Care Blood Sensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 May 23;14(6):266. doi: 10.3390/bios14060266. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38920570 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Polymer Science and Fabrication Processes for Enhanced Microfluidic Applications: An Overview.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Sep 6;15(9):1137. doi: 10.3390/mi15091137. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing diagnostics and disease modeling: current concepts in biofabrication of soft microfluidic systems.In Vitro Model. 2024 Jun 4;3(2-3):139-150. doi: 10.1007/s44164-024-00072-5. eCollection 2024 Jun. In Vitro Model. 2024. PMID: 39872940 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances and Challenges in 3D Bioprinted Cancer Models: Opportunities for Personalized Medicine and Tissue Engineering.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;17(7):948. doi: 10.3390/polym17070948. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40219336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Numerical models for organ-on-a-chip: A systematic review and analyses.Biomicrofluidics. 2025 Jul 1;19(4):041501. doi: 10.1063/5.0260477. eCollection 2025 Jul. Biomicrofluidics. 2025. PMID: 40612531 Review.
-
Innovative Micro- and Nano-Architectures in Biomedical Engineering for Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;16(4):419. doi: 10.3390/mi16040419. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Platform for Predicting Nanoparticle Dynamics in Cancer Therapeutics.J Fluoresc. 2025 Aug 11. doi: 10.1007/s10895-025-04453-1. Online ahead of print. J Fluoresc. 2025. PMID: 40788556
-
Effects of Process Parameters on Pulsed Laser Micromachining for Glass-Based Microfluidic Devices.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jun 5;18(11):2657. doi: 10.3390/ma18112657. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stone H.A., Stroock A.D., Ajdari A. Engineering Flows in Small Devices: Microfluidics toward a Lab-on-a-Chip. Annu. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 2004;36:381–411. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.36.050802.122124. - DOI
-
- Luísa V., Faustino C. Microfluidic System for Cell Separation and Deformation Assessment by Using Passive Methods. [(accessed on 22 May 2024)]. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1822/80141.
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 2022.02085.PTDC/Foundation for Science and Technology
- 2022.06207.PTDC/Foundation for Science and Technology
- PTDC/EEI-EEE/2846/2021/Foundation for Science and Technology
- UIDB/04436/2020/Foundation for Science and Technology
- UIDP/04436/2020/Foundation for Science and Technology
- UIDB/04077/2020/Foundation for Science and Technology
- UIDP/04077/2020/Foundation for Science and Technology
- UIDB/00532/2020/Foundation for Science and Technology
- UIDB/00690/2020/Foundation for Science and Technology
- UIDB/04650/2020/Foundation for Science and Technology
- LA/P/0045/2020/Foundation for Science and Technology
- 2021.00027.CEECIND/CP1664/CT0007/Foundation for Science and Technology
- UI/BD/151028/2021/Foundation for Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

