Endoscopic Advances in the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- PMID: 39064549
- PMCID: PMC11278532
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina60071120
Endoscopic Advances in the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Abstract
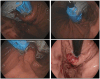
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is one of the most common diseases that occurs secondary to failure of the antireflux barrier system, resulting in the frequent and abnormal reflux of gastric contents to the esophagus. GERD is diagnosed in routine clinical practice based on the classic symptoms of heartburn and regurgitation. However, a subset of patients with atypical symptoms can pose challenges in diagnosing GERD. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is the most common initial diagnostic test used in the assessment for GERD, although half of these patients will not have any positive endoscopic findings suggestive of GERD. The advanced endoscopic techniques have improved the diagnostic yield of GERD diagnosis and its complications, such as Barrett's esophagus and early esophageal adenocarcinoma. These newer endoscopic tools can better detect subtle irregularities in the mucosa and vascular structures. The management options for GERD include lifestyle modifications, pharmacological therapy, and endoscopic and surgical interventions. The latest addition to the armamentarium is the minimally invasive endoscopic interventions in carefully selected patients, including the electrical stimulation of the LES, Antireflux mucosectomy, Radiofrequency therapy, Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication, Endoscopic Full-Thickness plication (GERDx™), and suturing devices. With the emergence of these advanced endoscopic techniques, it is crucial to understand their selection criteria, advantages, and disadvantages.
Keywords: FICE; GERD; I-scan; Narrow Band Imaging; endoscopy; esophageal capsule endoscopy; gastroesophageal reflux disease; transoral incisionless fundoplication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

