Efficacy of Dietary Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children and Adults: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39064673
- PMCID: PMC11279983
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16142231
Efficacy of Dietary Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children and Adults: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Several dietary approaches have been used to induce remission in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), yielding varied results.
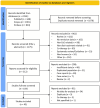
Methods: We searched the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Scopus databases up to May 2024 to identify studies including dietary interventions for EoE used as monotherapy. Summary estimates with 95% CIs for achieving <15 eosinophils/HPF were calculated for each approach. Fixed or random effects models were used depending on heterogeneity (I2); publication bias risks were assessed using funnel plot analyses. Subgroup analyses results were compared using meta-regression.
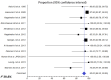
Results: Forty-three studies with 2825 patients were included in quantitative summaries. The overall rate of histologic remission was 60.6% (95% CI, 54.6-66.5%). Effectiveness rates were 94.5% (95% CI, 92.3-96.4%) for elemental diets, 63.9% (95% CI, 58.5-69.2%) for six-food elimination diets, 54.7% (95% CI, 45.7-63.6%) for four-food elimination diets, 44.3% (95% CI, 36.1-52.8%) for two-food elimination diets, 46.4% (95% CI, 40-52.9%) for one-food elimination diets, and 39.5% (95% CI, 30.3-49.2%) for allergy testing-directed food elimination diets. Overall, superior efficacy was noted in children than in adults and in retrospective compared to prospective studies.
Conclusion: Diet therapy remains an effective therapeutic asset for pediatric and adult patients with EoE, with increasing efficacy noted as the levels of dietary restriction increase.
Keywords: cohort studies; dietary treatment; eosinophilic esophagitis; histological remission; meta-analysis; pediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Lucendo A.J., Molina-Infante J., Arias A., von Arnim U., Bredenoord A.J., Bussmann C., Amil Dias J., Bove M., Gonzalez-Cervera J., Larsson H., et al. Guidelines on Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Evidence-Based Statements and Recommendations for Diagnosis and Management in Children and Adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017;5:335–358. doi: 10.1177/2050640616689525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kagalwalla A.F., Shah A., Li B.U.K., Sentongo T.A., Ritz S., Manuel-Rubio M., Jacques K., Wang D., Melin-Aldana H., Nelson S.P. Identification of Specific Foods Responsible for Inflammation in Children with Eosinophilic Esophagitis Successfully Treated with Empiric Elimination Diet. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011;53:145–149. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31821cf503. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

