Revealing the Potency of Growth Factors in Bovine Colostrum
- PMID: 39064802
- PMCID: PMC11279796
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16142359
Revealing the Potency of Growth Factors in Bovine Colostrum
Abstract
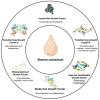
Colostrum is a nutritious milk synthesized by mammals during the postpartum period, and its rich bioactive components has led to a global increase in the consumption of bovine colostrum as a supplement. Bovine colostrum contains key components such as immunoglobulins, oligosaccharides, lactoferrin and lysozyme. It is a special supplement source due to its natural, high bioavailability and high concentrations of growth factors. Growth factors are critical to many physiological functions, and considering its presence in the colostrum, further research must be conducted on its safe application in many bodily disorders. Growth factors contribute to wound healing, muscle and bone development, and supporting growth in children. Additionally, the molecular mechanisms have been explored, highlighting the growth factors roles in cell proliferation, tissue regeneration, and the regulation of immune responses. These findings are crucial for understanding the potential health effects of bovine colostrum, ensuring its safe use, and forming a basis for future clinical applications. This review article examines the growth factors concentration in bovine colostrum, their benefits, clinical studies, and molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: colostrum; growth factors; health benefits; immune responses; nutritional supplements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yalçıntaş Y.M., Baydemir B., Duman H., Eker F., Bayraktar Biçen A., Ertürk M., Karav S. Exploring the Impact of Colostrum Supplementation on Athletes: A Comprehensive Analysis of Clinical Trials and Diverse Properties. Front. Immunol. 2024;15:1395437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395437. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

