The TRPA1 Ion Channel Mediates Oxidative Stress-Related Migraine Pathogenesis
- PMID: 39064963
- PMCID: PMC11280075
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29143385
The TRPA1 Ion Channel Mediates Oxidative Stress-Related Migraine Pathogenesis
Abstract
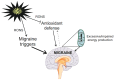
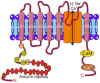
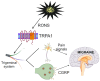
Although the introduction of drugs targeting calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) revolutionized migraine treatment, still a substantial proportion of migraine patients do not respond satisfactorily to such a treatment, and new therapeutic targets are needed. Therefore, molecular studies on migraine pathogenesis are justified. Oxidative stress is implicated in migraine pathogenesis, as many migraine triggers are related to the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS). Migraine has been proposed as a superior mechanism of the brain to face oxidative stress resulting from energetic imbalance. However, the precise mechanism behind the link between migraine and oxidative stress is not known. Nociceptive primary afferent nerve fiber endings express ion channel receptors that change harmful stimuli into electric pain signals. Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily A member 1 (TRPA1) is an ion channel that can be activated by oxidative stress products and stimulate the release of CGRP from nerve endings. It is a transmembrane protein with ankyrin repeats and conserved cysteines in its N-terminus embedded in the cytosol. TRPA1 may be a central element of the signaling pathway from oxidative stress and NO production to CGRP release, which may play a critical role in headache induction. In this narrative review, we present information on the role of oxidative stress in migraine pathogenesis and provide arguments that TRPA1 may be "a missing link" between oxidative stress and migraine and therefore a druggable target in this disease.
Keywords: TRPA1; calcitonin gene-related peptide; migraine; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
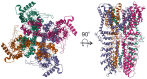
Similar articles
-
ROS/TRPA1/CGRP signaling mediates cortical spreading depression.J Headache Pain. 2019 Mar 6;20(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s10194-019-0978-z. J Headache Pain. 2019. PMID: 30841847 Free PMC article.
-
The TRPA1 channel in migraine mechanism and treatment.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 May;171(10):2552-67. doi: 10.1111/bph.12512. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24206166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Connections of the TRPA1 Ion Channel in Pain Transmission and Neurogenic Inflammation - a Therapeutic Perspective in Migraine?Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;60(10):5578-5591. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03428-2. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37326902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of chronic headache].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2024;124(10):35-40. doi: 10.17116/jnevro202412410135. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2024. PMID: 39575957 Review. Russian.
-
Acetaldehyde via CGRP receptor and TRPA1 in Schwann cells mediates ethanol-evoked periorbital mechanical allodynia in mice: relevance for migraine.J Biomed Sci. 2023 Apr 26;30(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00922-6. J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 37101198 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation.Open Med (Wars). 2025 May 17;20(1):20251201. doi: 10.1515/med-2025-1201. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40391079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gender-different effect of Src family kinases antagonism on photophobia and trigeminal ganglion activity.J Headache Pain. 2024 Oct 11;25(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01875-3. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39390364 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanotransduction in Development: A Focus on Angiogenesis.Biology (Basel). 2025 Mar 27;14(4):346. doi: 10.3390/biology14040346. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

