Cancer Chemopreventive Effect of 2',4'-Dihydroxy-6'-methoxy-3',5'-dimethylchalcone on Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Early Stages of Hepatocarcinogenesis in Rats
- PMID: 39065504
- PMCID: PMC11280862
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13141975
Cancer Chemopreventive Effect of 2',4'-Dihydroxy-6'-methoxy-3',5'-dimethylchalcone on Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Early Stages of Hepatocarcinogenesis in Rats
Abstract
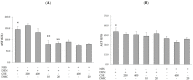
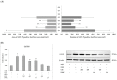
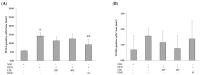
2',4'-dihydroxy-6'-methoxy-3',5'-dimethylchalcone (DMC) is a major compound in Cleistocalyx nervosum seed extract (CSE), which has been reported to have various biological activities, including anti-cancer activity. Therefore, this study attempted to evaluate whether DMC is a chemopreventive compound in CSE. Moreover, the preventive mechanisms of CSE and DMC in the DEN-induced early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis in rats were investigated. Male Wistar rats were intraperitoneally injected with DEN 50 mg/kg bw once a week for 8 weeks. Rats received CSE and DMC orally throughout the experiment. The number of glutathione S-transferase placental form (GST-P)-positive foci in the liver was measured. Furthermore, the preventive mechanisms of CSE and DMC on DEN-induced HCC, including cell proliferation and apoptosis, were investigated. Administering CSE at a dosage of 400 mg/kg bw and DMC at a dosage of 10 mg/kg bw significantly decreased the number and size of GST-P-positive foci and GST-P expression. In addition, DMC inhibited the development of preneoplastic lesions by decreasing cell proliferation and causing cell apoptosis; however, CSE inhibited the development of preneoplastic lesions by inducing cell apoptosis. In conclusion, DMC exhibited a cancer chemopreventive effect on the early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis by increasing cell apoptosis and reducing cell proliferation.
Keywords: 2′,4′-dihydroxy-6′-methoxy-3′,5′-dimethylchalcone; Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala seed; cancer chemoprevention; hepatocarcinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Low-polar extract from seed of Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala modulates initiation and promotion stages of chemically-induced carcinogenesis in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jan;133:110963. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110963. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33190034
-
2,4'-dihydroxy-6'-methoxy-3',5'-dimethylchalcone from Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala seeds attenuated the early stage of diethylnitrosamine and 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colorectal carcinogenesis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Sep;165:115221. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115221. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37517291
-
Cancer chemopreventive effect of Spirogyra neglecta (Hassall) Kützing on diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(4):1611-6. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.4.1611. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24641376
-
Cancer chemopreventive potential of cooked glutinous purple rice on the early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis in rats.Front Nutr. 2022 Dec 21;9:1032771. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1032771. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36618678 Free PMC article.
-
Cleistocalyx nervosum extract ameliorates chemical-induced oxidative stress in early stages of rat hepatocarcinogenesis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(6):2825-30. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.6.2825. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24761908
Cited by
-
The Effect of the Ethanolic Extracts from Syzygium aromaticum and Syzygium nervosum on Antiproliferative Activity and Apoptosis in HCT116 and HT-29 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 16;26(14):6826. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146826. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moye-Holz D., Ewen M., Dreser A., Bautista-Arredondo S., Soria-Saucedo R., van Dijk J.P., Reijneveld S.A., Hogerzeil H.V. Availability, prices, and affordability of selected essential cancer medicines in a middle-income country—The case of Mexico. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2020;20:424. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05167-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

