Investigation of Factors Influencing the Effectiveness of Deformable Nanovesicles for Insulin Nebulization Inhalation
- PMID: 39065576
- PMCID: PMC11280345
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070879
Investigation of Factors Influencing the Effectiveness of Deformable Nanovesicles for Insulin Nebulization Inhalation
Abstract
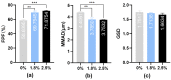
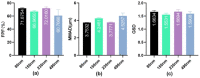
Nebulized inhalation offers a noninvasive method for delivering drugs to treat both local respiratory and systemic diseases. In this study, insulin was used as a model drug to design a series of deformable nanovesicles (DNVs) with key quality attributes, including particle size, deformability, and drug load capacity. We investigated the effects of these properties on aerosol generation, macrophage phagocytosis, and bloodstream penetration. The results showed that deformability improved nebulization performance and reduced macrophage phagocytosis, benefiting local and systemic delivery. However, the advantage of DNVs for transmembrane penetration was not evident in the alveolar epithelium. Within the size range of 80-490 nm, the smaller the particle size of IPC-DNVs, the easier it is to evade clearance by macrophages and the more effective the in vivo hypoglycemic efficacy will be. In the drug load range of 3-5 mg/mL, a lower drug load resulted in better hypoglycemic efficacy. The area above the blood glucose decline curve with time (AAC) of nebulized DNVs was 2.32 times higher than that of the insulin solution, demonstrating the feasibility and advantages of DNVs in the pulmonary delivery of biomacromolecule drugs. This study provides insights into the construction and formulation optimization of pulmonary delivery carriers.
Keywords: biomacromolecule; deformable nanovesicles; influencing factors; nebulized inhalation.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Yiyue Guo are employed by the Beijing Wehand-Bio Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

