The Evolving Paradigm of Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting the ErbB/HER Family of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
- PMID: 39065587
- PMCID: PMC11279420
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070890
The Evolving Paradigm of Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting the ErbB/HER Family of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
Abstract
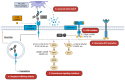
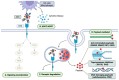
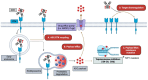
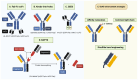
Current therapies targeting the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) family, including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), are limited by drug resistance and systemic toxicities. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are one of the most rapidly expanding classes of anti-cancer therapeutics with 13 presently approved by the FDA. Importantly, ADCs represent a promising therapeutic option with the potential to overcome traditional HER-targeted therapy resistance by delivering highly potent cytotoxins specifically to HER-overexpressing cancer cells and exerting both mAb- and payload-mediated antitumor efficacy. The clinical utility of HER-targeted ADCs is exemplified by the immense success of HER2-targeted ADCs including trastuzumab emtansine and trastuzumab deruxtecan. Still, strategies to improve upon existing HER2-targeted ADCs as well as the development of ADCs against other HER family members, particularly EGFR and HER3, are of great interest. To date, no HER4-targeting ADCs have been reported. In this review, we extensively detail clinical-stage EGFR-, HER2-, and HER3-targeting monospecific ADCs as well as novel clinical and pre-clinical bispecific ADCs (bsADCs) directed against this receptor family. We close by discussing nascent trends in the development of HER-targeting ADCs, including novel ADC payloads and HER ligand-targeted ADCs.
Keywords: EGFR; HER2; HER3; antibody–drug conjugates; bispecific antibodies; combination therapy; drug resistance; receptor tyrosine kinase; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guix M., Faber A.C., Wang S.E., Olivares M.G., Song Y., Qu S., Rinehart C., Seidel B., Yee D., Arteaga C.L., et al. Acquired Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Cancer Cells Is Mediated by Loss of IGF-Binding Proteins. J. Clin. Investig. 2008;118:2609–2619. doi: 10.1172/JCI34588. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

