Harnessing Potential of ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid with Nanotechnology for Enhanced Breast Cancer Therapy: A Comprehensive Investigation into ALA-Based Liposomal PTX Delivery
- PMID: 39065610
- PMCID: PMC11279858
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070913
Harnessing Potential of ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid with Nanotechnology for Enhanced Breast Cancer Therapy: A Comprehensive Investigation into ALA-Based Liposomal PTX Delivery
Abstract
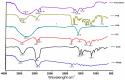
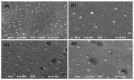
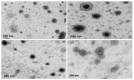
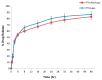
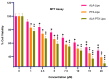
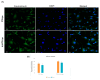
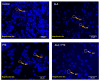
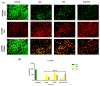
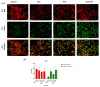
Our hypothesis posited that incorporating alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) into liposomes containing Paclitaxel (PTX) could augment cellular uptake, decrease the therapeutic dosage, and alleviate PTX-related side effects. Our investigation encompassed characterization of the liposomal formulation, encompassing aspects like particle size, surface morphology, chemical structure, drug release kinetics, and stability. Compatibility studies were performed through Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). By utilizing the Box-Behnken design (BBD), we developed ALA-based liposomes with satisfactory particle size and entrapment efficiency. It is noteworthy that ALA incorporation led to a slight increase in particle size but did not notably affect drug entrapment. In vitro drug release assessments unveiled a sustained release pattern, with ALA-PTX liposomes demonstrating release profiles comparable to PTX liposomes. Morphological examinations confirmed the spherical structure of the liposomes, indicating that substituting ALA with phosphatidylcholine did not alter the physicochemical properties. Cellular uptake investigations showcased enhanced uptake of ALA-based liposomes in contrast to PTX liposomes, likely attributed to the heightened fluidity conferred by ALA. Efficacy against MCF-7 cells demonstrated concentration-dependent reductions in cell viability, with ALA-PTX liposomes exhibiting the lowest IC50 value. Morphological analysis confirmed apoptotic changes in cells treated with all formulations, with ALA-PTX liposomes eliciting more pronounced changes, indicative of enhanced anticancer efficacy.
Keywords: cancer; cell culture; liposome; paclitaxel; α-linolenic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paclitaxel and curcumin coadministration in novel cationic PEGylated niosomal formulations exhibit enhanced synergistic antitumor efficacy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 Mar 23;16(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0351-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29571289 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor Activity of α-Linolenic Acid-Paclitaxel Conjugate Nanoparticles: In vitro and in vivo.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Oct 27;16:7269-7281. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S331578. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34737564 Free PMC article.
-
Development of paclitaxel-loaded liposomal nanocarrier stabilized by triglyceride incorporation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Sep 6;11:4465-4477. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S113723. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27660440 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental design of a liposomal lipid system: A potential strategy for paclitaxel-based breast cancer treatment.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015 Dec 1;136:553-61. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.09.055. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015. PMID: 26454545
-
Liposomal paclitaxel formulations.J Control Release. 2012 Nov 10;163(3):322-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.09.006. Epub 2012 Sep 15. J Control Release. 2012. PMID: 22989535 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging nanostructure-based strategies for breast cancer therapy: innovations, challenges, and future directions.Med Oncol. 2025 Apr 30;42(6):188. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02743-z. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40307624 Review.
-
Structural Dynamics of OATP1A2 in Mediating Paclitaxel Transport Mechanism in Breast Cancer.Nanotheranostics. 2025 Feb 3;9(1):52-62. doi: 10.7150/ntno.103095. eCollection 2025. Nanotheranostics. 2025. PMID: 40078312 Free PMC article.
-
Liposomes and Their Therapeutic Applications in Enhancing Psoriasis and Breast Cancer Treatments.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Nov 1;14(21):1760. doi: 10.3390/nano14211760. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39513840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HER-2 Receptor and αvβ3 Integrin Dual-Ligand Surface-Functionalized Liposome for Metastatic Breast Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 27;16(9):1128. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091128. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mansara P.P., Deshpande R.A., Vaidya M.M., Kaul-Ghanekar R. Differential ratios of omega fatty acids (AA/EPA+ DHA) modulate growth, lipid peroxidation and expression of tumor regulatory MARBPs in breast cancer cell lines MCF7 and MDA-MB-231. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0136542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136542. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

