Lentisk (Pistacia lentiscus) Oil Nanoemulsions Loaded with Levofloxacin: Phytochemical Profiles and Antibiofilm Activity against Staphylococcus spp
- PMID: 39065624
- PMCID: PMC11280327
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070927
Lentisk (Pistacia lentiscus) Oil Nanoemulsions Loaded with Levofloxacin: Phytochemical Profiles and Antibiofilm Activity against Staphylococcus spp
Abstract
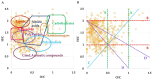
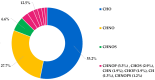
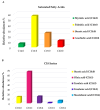
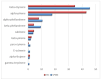
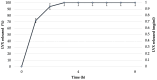
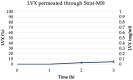
Most clinical isolates of both Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis show the capacity to adhere to abiotic surfaces and to develop biofilms resulting in a contribution to chronic human skin infections. Antibiotic resistance and poor biofilm penetration are the main causes of ineffective therapeutic treatment in killing bacteria within biofilms. A possible strategy could be represented by drug delivery systems, such as nanoemulsions (composed of bioactive oil, surfactant and water phase), which are useful for enhancing the drug permeation of a loaded drug inside the biofilm and its activity. Phytochemical characterization of Pistacia lentiscus oil (LO) by direct infusion Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR MS) allowed the identification of bioactive compounds with antimicrobial properties, including fatty acids and phenolic compounds. Several monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes have been also detected and confirmed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometric (GC-MS) analysis, together providing a complete metabolomic profiling of LO. In the present study, a nanoemulsion composed of LO has been employed for improving Levofloxacin water solubility. A deep physical-chemical characterization of the nanoemulsion including hydrodynamic diameter, ζ-potential, morphology, entrapment efficiency, stability release and permeation studies was performed. Additionally, the antimicrobial/antibiofilm activity of these preparations was evaluated against reference and clinical Staphylococcus spp. strains. In comparison to the free-form antibiotic, the loaded NE nanocarriers exhibited enhanced antimicrobial activity against the sessile forms of Staphylococcus spp. strains.
Keywords: Pistacia lentiscus L.; Staphylococcus spp.; antibiofilm activity; bioactive oil; mass spectrometry; nanoemulsion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytochemical Characterization and Effects on Cell Proliferation of Lentisk (Pistacia lentiscus) Berry Oil: a Revalued Source of Phenolics.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2020 Dec;75(4):487-494. doi: 10.1007/s11130-020-00835-x. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32671681
-
Antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects of shikonin with tea tree oil nanoemulsion against Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus.Biofouling. 2023 Oct-Nov;39(9-10):962-979. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2023.2281511. Epub 2023 Nov 26. Biofouling. 2023. PMID: 38009008
-
The Selective Interaction of Pistacia lentiscus Oil vs. Human Streptococci, an Old Functional Food Revisited with New Tools.Front Microbiol. 2017 Oct 24;8:2067. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02067. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29114245 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress of chemical constituents and biological activities of essential oil of Pistacia lentiscus].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Sep;44(17):3684-3694. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190529.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31602940 Review. Chinese.
-
A Review of Pistacia lentiscus Polyphenols: Chemical Diversity and Pharmacological Activities.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 7;12(2):279. doi: 10.3390/plants12020279. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678991 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antibiofilm and Antihemolytic Activities of Actinostemma lobatum Extract Rich in Quercetin against Staphylococcus aureus.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 16;16(8):1075. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081075. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204420 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular Carriers for Phytochemical Delivery: A Comprehensive Review of Techniques and Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 2;17(4):464. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040464. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

