Solid-State NMR Characterization of Mefloquine Resinate Complexes Designed for Taste-Masking Pediatric Formulations
- PMID: 39065722
- PMCID: PMC11280060
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17070870
Solid-State NMR Characterization of Mefloquine Resinate Complexes Designed for Taste-Masking Pediatric Formulations
Abstract
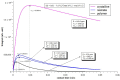
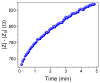
Mefloquine (MQ) is an antimalarial medication prescribed to treat or malaria prevention.. When taken by children, vomiting usually occurs, and new doses of medication frequently need to be taken. So, developing pediatric medicines using taste-masked antimalarial drug complexes is mandatory for the success of mefloquine administration. The hypothesis that binding mefloquine to an ion-exchange resin (R) could circumvent the drug's bitter taste problem was proposed, and solid-state 13C cross-polarization magic angle spinning (CPMAS) NMR was able to follow MQ-R mixtures through chemical shift and relaxation measurements. The nature of MQ-R complex formation could then be determined. Impedimetric electronic tongue equipment also verified the resinate taste-masking efficiency in vitro. Variations in chemical shifts and structure dynamics measured by proton relaxation properties (e.g., T1ρH) were used as probes to follow the extension of mixing and specific interactions that would be present in MQ-R. A significant decrease in T1ρH values was observed for MQ carbons in MQ-R complexes, compared to the ones in MQ (from 100-200 ms in MQ to 20-50 ms in an MQ-R complex). The results evidenced that the cationic resin interacts strongly with mefloquine molecules in the formulation of a 1:1 ratio complex. Thus, 13C CPMAS NMR allowed the confirmation of the presence of a binding between mefloquine and polacrilin in the MQ-R formulation studied.
Keywords: 13C NMR; CPMAS NMR; T1ρH relaxation time; electronic tongue; ion-exchange resin; mefloquine; taste masking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Malaria treatment and prevention in pregnancy: indications for use and adverse events associated with use of chloroquine or mefloquine.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1996;55(1 Suppl):50-6. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1996.55.50. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1996. PMID: 8702037
-
Formulation and evaluation of Pheroid vesicles containing mefloquine for the treatment of malaria.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;66(1):14-22. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12147. Epub 2013 Oct 13. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24117456
-
Formulation and evaluation of meloxicam oral disintegrating tablet with dissolution enhanced by combination of cyclodextrin and ion exchange resins.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2015 Jun;41(6):1006-16. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2014.922573. Epub 2014 May 28. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2015. PMID: 24865111 Clinical Trial.
-
Investigation of Chloroquine Resinate Feasibility and In Vitro Taste Masking Evaluation for Pediatric Formulations.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022 Feb 2;23(2):69. doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02219-7. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022. PMID: 35112208
-
Intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy with mefloquine in HIV-infected women receiving cotrimoxazole prophylaxis: a multicenter randomized placebo-controlled trial.PLoS Med. 2014 Sep 23;11(9):e1001735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001735. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Med. 2014. PMID: 25247995 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Prado V.M., Queiroz T.B., Sá P.M., Seiceira R.C., Boechat N., Ferreira F.F. Mechanochemistry for the production of a hybrid salt used in the treatment of malaria. Green Chem. 2020;22:54–61. doi: 10.1039/C9GC02478F. - DOI
-
- Ranmal S.R., Lavarde M., Wallon E., Issa S., Taylor W.R., Nguyen Ngoc Pouplin J.L.A., Tuleu C., Pense-Lheritier A.M. Responsive Sensory Evaluation to Develop Flexible Taste-Masked Paediatric Primaquine Tablets against Malaria for Low-Resource Settings. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15:1879. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071879. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

