Oral Nanoformulations in Cardiovascular Medicine: Advances in Atherosclerosis Treatment
- PMID: 39065770
- PMCID: PMC11279631
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17070919
Oral Nanoformulations in Cardiovascular Medicine: Advances in Atherosclerosis Treatment
Abstract
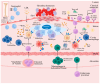
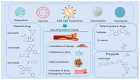
Atherosclerosis (AS) is the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of the arteries, causing them to narrow. If this occurs in the coronary arteries, the blood vessels may be completely blocked, resulting in myocardial infarction; if it occurs in the blood vessels of the brain, the blood vessels may be blocked, resulting in cerebral infarction, i.e., stroke. Studies have shown that the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis involves the processes of inflammation, lipid infiltration, oxidative stress, and endothelial damage, etc. SIRT, as a key factor regulating the molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress, inflammation, and aging, has an important impact on the pathogenesis of plaque formation, progression, and vulnerability. Statistics show that AS accounts for about 50 per cent of deaths in Western countries. Currently, oral medication is the mainstay of AS treatment, but its development is limited by side effects, low bioavailability and other unfavourable factors. In recent years, with the rapid development of nano-preparations, researchers have combined statins and natural product drugs within nanopreparations to improve their bioavailability. Based on this, this paper summarises the main pathogenesis of AS and also proposes new oral nanoformulations such as liposomes, nanoparticles, nanoemulsions, and nanocapsules to improve their application in the treatment of AS.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; nanopreparations; new drug delivery systems; oral medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of sirtuins in attenuating plaque vulnerability in atherosclerosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Jan;479(1):51-62. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04714-2. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 36952068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Delivery of Nanoparticles to Blood Vessels for the Treatment of Atherosclerosis.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 6;12(7):1504. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071504. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Injectable liposomal docosahexaenoic acid alleviates atherosclerosis progression and enhances plaque stability.J Control Release. 2023 Aug;360:344-364. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.06.035. Epub 2023 Jul 7. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37406819
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) and PARP Inhibitors: Mechanisms of Action and Role in Cardiovascular Disorders.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018 Dec;18(6):493-506. doi: 10.1007/s12012-018-9462-2. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29968072 Review.
-
Herbal Nanoformulations for Asthma Treatment.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(1):46-57. doi: 10.2174/1381612827666210929113528. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 34587880 Review.
Cited by
-
The relevance of resveratrol in ameliorating carotid atherosclerosis through glycolysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Apr 21;25(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04735-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40259219 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of lipid metabolism related immune markers in atherosclerosis through machine learning and experimental analysis.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 25;16:1549150. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1549150. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40070840 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted drug delivery systems for atherosclerosis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Apr 23;23(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03384-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40269931 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 82003985/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020M670825,2020T130568/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 20210204013YY, 20230401062YY/Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Project in China
- 202210199004,202210199011X/National College Students' innovation and entrepreneurship training program
- 2023C027-3/Jilin Provincial Development and Reform Commission program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials