On-Road Evaluation of Unobtrusive In-Car Respiration Monitoring
- PMID: 39065897
- PMCID: PMC11280551
- DOI: 10.3390/s24144500
On-Road Evaluation of Unobtrusive In-Car Respiration Monitoring
Abstract
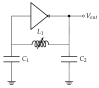
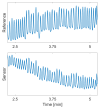
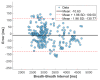
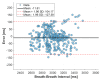
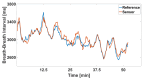
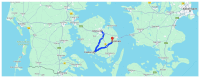
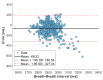
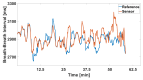
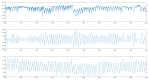
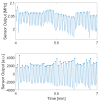
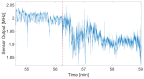
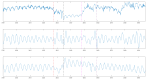
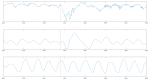
This paper introduces and evaluates an innovative sensor for unobtrusive in-car respiration monitoring, mounted on the backrest of the driver's seat. The sensor seamlessly integrates into the vehicle, measuring breathing rates continuously without requiring active participation from the driver. The paper proves the feasibility of unobtrusive in-car measurements over long periods of time. Operation of the sensor was investigated over 12 participants sitting in the driver seat. A total of 107 min of driving in diverse conditions with overall coverage rate of 84.45% underscores the sensor potential to reliably capture physiological changes in breathing rate for fatigue and stress detection.
Keywords: automotive sensors; breathing rate; continuous health monitoring; unobtrusive monitoring; vital signs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Quantitative Method to Guide the Integration of Textile Inductive Electrodes in Automotive Applications for Respiratory Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Nov 23;24(23):7483. doi: 10.3390/s24237483. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39686021 Free PMC article.
-
On-Road Evaluation of an Unobtrusive In-Vehicle Pressure-Based Driver Respiration Monitoring System.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 26;25(9):2739. doi: 10.3390/s25092739. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40363178 Free PMC article.
-
Unobtrusive in-car measurement of physiological signals on the road.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2024 Jul;2024:1-4. doi: 10.1109/EMBC53108.2024.10782515. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2024. PMID: 40039373
-
Unobtrusive Health Monitoring in Private Spaces: The Smart Vehicle.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Apr 25;20(9):2442. doi: 10.3390/s20092442. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32344815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Processing of physiological signals in automotive research.Biomed Tech (Berl). 2006 Dec;51(5-6):320-4. doi: 10.1515/BMT.2006.064. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2006. PMID: 17155867 Review.
Cited by
-
A Quantitative Method to Guide the Integration of Textile Inductive Electrodes in Automotive Applications for Respiratory Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Nov 23;24(23):7483. doi: 10.3390/s24237483. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39686021 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal Cameras for Continuous and Contactless Respiration Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Dec 19;24(24):8118. doi: 10.3390/s24248118. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On-Road Evaluation of an Unobtrusive In-Vehicle Pressure-Based Driver Respiration Monitoring System.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 26;25(9):2739. doi: 10.3390/s25092739. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40363178 Free PMC article.
-
Biomedical Signal Processing and Health Monitoring Based on Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 22;25(3):641. doi: 10.3390/s25030641. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943280 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory Monitoring with Textile Inductive Electrodes in Driving Applications: Effect of Electrode's Positioning and Form Factor on Signal Quality.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 25;25(7):2035. doi: 10.3390/s25072035. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Q., Chen X., Zhan Q., Yang T., Xia S. Respiration-based emotion recognition with deep learning. Comput. Ind. 2017;92:84–90. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2017.04.005. - DOI
-
- Cho Y., Bianchi-Berthouze N., Julier S.J. DeepBreath: Deep learning of breathing patterns for automatic stress recognition using low-cost thermal imaging in unconstrained settings; Proceedings of the 2017 Seventh International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII); San Antonio, TX, USA. 23–26 October 2017; Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE; 2017. pp. 456–463.
-
- Solaz J., Laparra-Hernández J., Bande D., Rodríguez N., Veleff S., Gerpe J., Medina E. Drowsiness detection based on the analysis of breathing rate obtained from real-time image recognition. Transp. Res. Procedia. 2016;14:3867–3876. doi: 10.1016/j.trpro.2016.05.472. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

