The Impact of Liquids and Saturated Salt Solutions on Polymer-Coated Fiber Optic Sensors for Distributed Strain and Temperature Measurement
- PMID: 39066056
- PMCID: PMC11281284
- DOI: 10.3390/s24144659
The Impact of Liquids and Saturated Salt Solutions on Polymer-Coated Fiber Optic Sensors for Distributed Strain and Temperature Measurement
Abstract
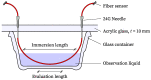
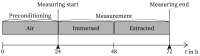
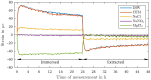
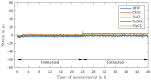
The application of distributed fiber optic strain and temperature measurement can be utilized to address a multitude of measurement tasks across a diverse range of fields, particularly in the context of structural health monitoring in the domains of building construction, civil engineering, and special foundation engineering. However, a comprehensive understanding of the influences on the measurement method and the sensors is essential to prevent misinterpretations or measurement deviations. In this context, this study investigated the effects of moisture exposure, including various salt solutions and a high pH value, on a distributed strain measurement using Rayleigh backscattering. Three fiber optic sensors with different coating materials and one uncoated fiber were exposed to five different solutions for 24 h. The study revealed significant discrepancies (∼38%) in deformation between the three coating types depending on the surrounding solution. Furthermore, in contrast to the prevailing literature, which predominantly describes swelling effects, a negative deformation (∼-47 με) was observed in a magnesium chloride solution. The findings of this study indicate that corresponding effects can impact the precision of measurement, potentially leading to misinterpretations. Conversely, these effects could be used to conduct large-scale monitoring of chemical components using distributed fiber optic sensing.
Keywords: DFOS; SHM (Structural Health Monitoring); distributed fiber optic sensing; fiber coating; fiber optic sensor; strain measurement; temperature measurement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Barrias A., Rius J.R.C., Herrero S.V. Fatigue testing of reinforced concrete beam instrumented with distributed optical fiber sensors (DOFS) Civ. Eng. Res. Irel. 2018:729–734.
-
- Zdanowicz K., Gebauer D., Koschemann M., Speck K., Steinbock O., Beckmann B., Marx S. Distributed fiber optic sensors for measuring strains of concrete, steel, and textile reinforcement: Possible fields of application. Struct. Concr. 2022;23:3367–3382. doi: 10.1002/suco.202100689. - DOI
-
- Ashry I., Mao Y., Wang B., Hveding F., Bukhamsin A.Y., Ng T.K., Ooi B.S. A Review of Distributed Fiber–Optic Sensing in the Oil and Gas Industry. J. Light. Technol. 2022;40:1407–1431. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2021.3135653. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

