Comparison of Routes of Administration, Frequency, and Duration of Favipiravir Treatment in Mouse and Guinea Pig Models of Ebola Virus Disease
- PMID: 39066263
- PMCID: PMC11281331
- DOI: 10.3390/v16071101
Comparison of Routes of Administration, Frequency, and Duration of Favipiravir Treatment in Mouse and Guinea Pig Models of Ebola Virus Disease
Abstract
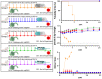
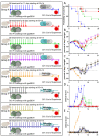
Favipiravir is a ribonucleoside analogue that has been explored as a therapeutic for the treatment of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD). Promising data from rodent models has informed nonhuman primate trials, as well as evaluation in patients during the 2013-2016 West African EVD outbreak of favipiravir treatment. However, mixed results from these studies hindered regulatory approval of favipiravir for the indication of EVD. This study examined the influence of route of administration, duration of treatment, and treatment schedule of favipiravir in immune competent mouse and guinea pig models using rodent-adapted Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV). A dose of 300 mg/kg/day of favipiravir with an 8-day treatment was found to be fully effective at preventing lethal EVD-like disease in BALB/c mice regardless of route of administration (oral, intraperitoneal, or subcutaneous) or whether it was provided as a once-daily dose or a twice-daily split dose. Preclinical data generated in guinea pigs demonstrates that an 8-day treatment of 300 mg/kg/day of favipiravir reduces mortality following EBOV challenge regardless of route of treatment or duration of treatments for 8, 11, or 15 days. This work supports the future translational development of favipiravir as an EVD therapeutic.
Keywords: EBOV; Ebola virus; T-705; animal model; favipiravir; filovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Feldmann H., Slenczka W., Klenk H.-D. Emerging and Reemerging of Filoviruses. Springer; Vienna, Austria: 1996. pp. 77–100. - PubMed
-
- Breman J.G., Heymann D.L., Lloyd G., McCormick J.B., Miatudila M., Murphy F.A., Muyembé-Tamfun J.-J., Piot P., Ruppol J.-F., Sureau P. Discovery and description of Ebola Zaire virus in 1976 and relevance to the West African epidemic during 2013–2016. J. Infect. Dis. 2016;214:S93–S101. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw207. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN272201700040I/ HHSN27200007/the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services
- HHSN272201700040I/ HHSN27200007/the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services
- HHSN272201700040I/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

