Assessing the mechanism of facilitated proton transport across GUVs trapped in a microfluidic device
- PMID: 39066477
- PMCID: PMC11428277
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.07.030
Assessing the mechanism of facilitated proton transport across GUVs trapped in a microfluidic device
Abstract
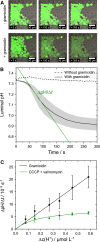
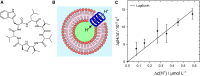
Proton transport across lipid membranes is one of the most fundamental reactions that make up living organisms. In vitro, however, the study of proton transport reactions can be very challenging due to limitations imposed by proton concentrations, compartment size, and unstirred layers as well as buffer exchange and buffer capacity. In this study, we have developed a proton permeation assay based on the microfluidic trapping of giant vesicles enclosing the pH-sensitive dye pyranine to address some of these challenges. Time-resolved fluorescence imaging upon a rapid pH shift enabled us to investigate the facilitated H+ permeation mediated by either a channel or a carrier. Specifically, we compared the proton transport rates as a function of different proton gradients of the channel gramicidin D and the proton carrier carbonyl cyanide-m-chlorophenyl hydrazone. Our results demonstrate the efficacy of the assay in monitoring proton transport reactions and distinguishing between a channel-like and a carrier-like mechanism. This groundbreaking result enabled us to elucidate the enigmatic mode of the proton permeation mechanism of the recently discovered natural fibupeptide lugdunin.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Vercellino I., Sazanov L.A. The assembly, regulation and function of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022;23:141–161. - PubMed
-
- Forrest L.R., Krämer R., Ziegler C. The structural basis of secondary active transport mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011;1807:167–188. - PubMed
-
- Jeuken L.J., Bushby R.J., Evans S.D. Proton transport into a tethered bilayer lipid membrane. Electrochem. Commun. 2007;9:610–614.
-
- Inoue K., Tahara S., et al. Kandori H. Spectroscopic study of proton-transfer mechanism of inward proton-pump rhodopsin, Parvularcula oceani xenorhodopsin. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2018;122:6453–6461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

