Specific targeting of cancer vaccines to antigen-presenting cells via an endogenous TLR2/6 ligand derived from cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase 1
- PMID: 39066478
- PMCID: PMC11489552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.07.014
Specific targeting of cancer vaccines to antigen-presenting cells via an endogenous TLR2/6 ligand derived from cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase 1
Abstract
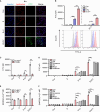
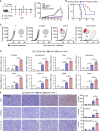
Cancer vaccines have been developed as a promising way to boost cancer immunity. However, their clinical potency is often limited due to the imprecise delivery of tumor antigens. To overcome this problem, we conjugated an endogenous Toll-like receptor (TLR)2/6 ligand, UNE-C1, to human papilloma virus type 16 (HPV-16)-derived peptide antigen, E7, and found that the UNE-C1-conjugated cancer vaccine (UCV) showed significantly enhanced antitumor activity in vivo compared with the noncovalent combination of UNE-C1 and E7. The combination of UCV with PD-1 blockades further augmented its therapeutic efficacy. Specifically, the conjugation of UNE-C1 to E7 enhanced its retention in inguinal draining lymph nodes, the specific delivery to dendritic cells and E7 antigen-specific T cell responses, and antitumor efficacy in vivo compared with the noncovalent combination of the two peptides. These findings suggest the potential of UNE-C1 derived from human cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase 1 as a unique vehicle for the specific delivery of cancer antigens to antigen-presenting cells via TLR2/6 for the improvement of cancer vaccines.
Keywords: Toll-like receptor 2; antigen uptake presentation; cancer vaccine; cervical cancer; conjugated vaccine; cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase; human papillomavirus 16; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immune stimulator; protein delivery.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.K. is an inventor on patents 10-2022-0070287 related to this paper and is a founder of Zymedi.
Figures




References
-
- Park M.C., Goughnour P.C., Jun S., Cho S., Song E., Kim S.B., Kim H.Y., Hyun J.K., Kim P., Jung H.S., Kim S. Two distinct receptor-binding domains of human glycyl-tRNA synthetase 1 displayed on extracellular vesicles activate M1 polarization and phagocytic bridging of macrophages to cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2022;539 doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215698. - DOI - PubMed

