Continuous Norming Approaches: A Systematic Review and Real Data Example
- PMID: 39066602
- PMCID: PMC12089670
- DOI: 10.1177/10731911241260545
Continuous Norming Approaches: A Systematic Review and Real Data Example
Abstract
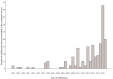
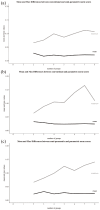
Norming of psychological tests is decisive for test score interpretation. However, conventional norming based on subgroups results either in biases or require very large samples to gather precise norms. Continuous norming methods, namely inferential, semi-parametric, and (simplified) parametric norming, propose to solve those issues. This article provides a systematic review of continuous norming. The review includes 121 publications with overall 189 studies. The main findings indicate that most studies used simplified parametric norming, not all studies considered essential distributional assumptions, and the evidence comparing different norming methods is inconclusive. In a real data example, using the standardization sample of the Need for Cognition-KIDS scale, we compared the precision of conventional, semi-parametric, and parametric norms. A hierarchy in terms of precision emerged with conventional norms being least precise, followed by semi-parametric norms, and parametric norms being most precise. We discuss these findings by comparing our findings and methods to previous studies.
Keywords: GAMLSS; cNORM; continuous norming; need for cognition; norm generation; regression-based norming; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Akaike H. (1974). A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 19(6), 716–723. 10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705 - DOI
-
- Akaike H. (1983). Statistical inference and measurement of entropy. In Box G. E. P., Leonard T., Wu C.-F. (Eds.), Scientific inference, data analysis, and robustness (pp. 165–189). Elsevier. 10.1016/B978-0-12-121160-8.50015-6 - DOI
-
- American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, & National Council on Measurement in Education. (2014). Standards for educational and psychological testing. American Educational Research Association.
-
- Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B., Walker S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
-
- Brandt H., Moosbrugger H. (2020). Planungsaspekte und Konstruktionsphasen von Tests und Fragebogen. In Moosbrugger H., Kelava A. (Eds.), Testtheorie und Fragebogenkonstruktion (pp. 39–66). Springer.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

