Structures and compositional dynamics of Mediator in transcription regulation
- PMID: 39067114
- PMCID: PMC11779508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2024.102892
Structures and compositional dynamics of Mediator in transcription regulation
Abstract
The eukaryotic Mediator, comprising a large Core (cMED) and a dissociable CDK8 kinase module (CKM), functions as a critical coregulator during RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) transcription. cMED recruits RNAPII and facilitates the assembly of the pre-initiation complex (PIC) at promoters. In contrast, CKM prevents RNAPII binding to cMED while simultaneously exerting positive or negative influence on gene transcription through its kinase function. Recent structural studies on cMED and CKM have revealed their intricate architectures and subunit interactions. Here, we explore these structures, providing a comprehensive insight into Mediator (cMED-CKM) architecture and its potential mechanism in regulating RNAPII transcription. Additionally, we discuss the remaining puzzles that require further investigation to fully understand how cMED coordinates with CKM to regulate transcription in various events.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
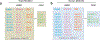
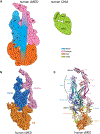
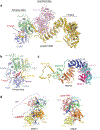
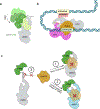
References
-
- Cramer P: Eukaryotic Transcription Turns 50. Cell 2019, 179:808–812. - PubMed
-
- Soutourina J: Mammalian Mediator as a Functional Link between Enhancers and Promoters. Cell 2019, 178:1036–1038. - PubMed
-
- Soutourina J: Transcription regulation by the Mediator complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 2018, 19:262–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

