Biomarkers for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (miR-24, miR-200, and miR-34): Screening and Detection MicroRNA
- PMID: 39068557
- PMCID: PMC11480605
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.7.2265
Biomarkers for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (miR-24, miR-200, and miR-34): Screening and Detection MicroRNA
Abstract
Introduction: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) includes about 90% of all oral malignant tumors, and most of them are diagnosed in advanced stages. This study investigated the expression changes of miR-24, miR-200, and miR-34 in saliva samples of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma, for early diagnosis.
Methods: In this study, 30 patients and 30 healthy individuals were selected. After RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis, the expression levels of miR-24, miR-200, and miR-34 in saliva samples were measured and evaluated using the Real-Time PCR technique.
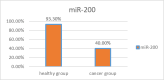
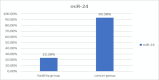
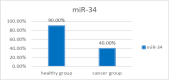
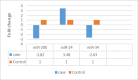
Results: Folding change calculation using 2^(-∆∆ Ct) refers to the relative difference in the expression of the markers of the two groups. The expression level of two biomarkers, miR-200 and miR-34, is decreased in patients compared to healthy people; and the expression level of miR-24 is increased in patients compared to healthy people.
Conclusion: In general, considering the availability and convenience of saliva sample collection for early detection of the disease, this research result can be considered a diagnostic screening test. To further prove the research results, conducting more extensive studies with more samples is recommended.
Keywords: Early Diagnosis; miR-200; miR-24; miR-34; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide study of salivary miRNAs identifies miR-423-5p as promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(6):2987-2999. doi: 10.7150/thno.45157. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33456584 Free PMC article.
-
"Salivary LINC00657 and miRNA-106a as diagnostic biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma, an observational diagnostic study".BMC Oral Health. 2023 Dec 12;23(1):994. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03726-0. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 38087258 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value and potential circulating of miR-99a as tumor suppressor biomarker in serum of oral squamous cell carcinoma and erosive atrophic lichen planus.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024 Jun;125(3S):101806. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2024.101806. Epub 2024 Feb 24. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38408642
-
A new perspective on diagnostic strategies concerning the potential of saliva-based miRNA signatures in oral cancer.Diagn Pathol. 2024 Nov 16;19(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13000-024-01575-1. Diagn Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39548527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of common salivary miRNA in oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 4;24(1):1177. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04986-0. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39367474 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Salivary miRNAs and cytokines associated with diagnosis and prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jan 22;13:1531016. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1531016. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39911325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding Salivary ncRNAomes as Novel Biomarkers for Oral Cancer Detection and Prognosis.Noncoding RNA. 2025 Mar 20;11(2):28. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11020028. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 40126352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding the Promise and Challenges of miRNA-Based Cancer Therapies: An Essential Update on miR-21, miR-34, and miR-155.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Oct 28;21(14):2781-2798. doi: 10.7150/ijms.102123. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39512697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging Saliva for Insights into Head and Neck Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 17;25(24):13514. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413514. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769275 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collins FS, Barker AD. Mapping the cancer genome. Sci Am. 2007;296(3):50–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

