Development and identification of a novel wheat-Thinopyrum ponticum disomic substitution line DS5Ag(5D) with new genes conferring resistance to powdery mildew and leaf rust
- PMID: 39069623
- PMCID: PMC11285282
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05433-6
Development and identification of a novel wheat-Thinopyrum ponticum disomic substitution line DS5Ag(5D) with new genes conferring resistance to powdery mildew and leaf rust
Abstract
Background: Powdery mildew (caused by Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici (Bgt)) and leaf rust (caused by Puccinia triticina (Pt)) are prevalent diseases in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) production. Thinopyrum ponticum (2n = 10x = 70, EeEeEbEbExExStStStSt) contains genes that confer high levels of resistance to these diseases.
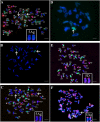
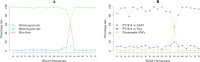
Results: An elite wheat-Th. ponticum disomic substitution line, DS5Ag(5D), was developed in the Bainong Aikang 58 (AK58) background. The line was assessed using genomic in situ hybridization (GISH), oligo-nucleotide probe multiplex (ONPM) fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and molecular markers. Twenty eight chromosome-specific molecular markers were identified for the alien chromosome, and 22 of them were co-dominant. Additionally, SNP markers from the wheat 660 K SNP chip were utilized to confirm chromosome identification and they provide molecular tools for tagging the chromosome in concern. The substitution line demonstrated high levels of resistance to powdery mildew throughout its growth period and to leaf rust at the adult stage. Based on the resistance evaluation of five F5 populations between the substitution lines and wheat genotypes with different levels of sensitivity to the two diseases. Results showed that the resistance genes located on 5Ag confered stable resistance against both diseases across different backgrounds. Resistance spectrum analysis combined with diagnostic marker detection of known resistance genes of Th. ponticum revealed that 5Ag contained two novel genes, Pm5Ag and Lr5Ag, which conferred resistance to powdery mildew and leaf rust, respectively.
Conclusions: In this study, a novel wheat-Th. ponticum disomic substitution line DS5Ag(5D) was successfully developed. The Th. ponticum chromosome 5Ag contain new resistance genes for powdery mildew and leaf rust. Chromosomic-specific molecular markers were generated and they can be used to track the 5Ag chromosome fragments. Consequently, this study provides new elite germplasm resources and molecular markers to facilitate the breeding of wheat varieties that is resistant to powdery mildew and leaf rust.
Keywords: Thinopyrum ponticum; Disomic substitution line; Fluorescence in situ hybridization; Leaf rust; Powdery mildew.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Lin G, Chen H, Tian B, Sehgal SK, Singh L, Xie J, Rawat N, Juliana P, Singh N, Shrestha S, et al. Cloning of the broadly effective wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr42 transferred from Aegilops tauschii. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3044. 10.1038/s41467-022-30784-9. 10.1038/s41467-022-30784-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

