Protective effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived secretome on dermonecrosis induced in rabbits by Loxosceles intermedia spider venom
- PMID: 39069986
- PMCID: PMC11276892
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2024-0004
Protective effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived secretome on dermonecrosis induced in rabbits by Loxosceles intermedia spider venom
Abstract
Background: Loxoscelism refers to a set of clinical manifestations caused by the bite of spiders from the Loxosceles genus. The classic clinical symptoms are characterized by an intense inflammatory reaction at the bite site followed by local necrosis and can be classified as cutaneous loxoscelism. This cutaneous form presents difficult healing, and the proposed treatments are not specific or effective. This study aimed to evaluate the protective effect of mesenchymal stromal cells-derived secretome on dermonecrosis induced by Loxosceles intermedia spider venom in rabbits.
Methods: Sixteen rabbits were distributed into four groups (n = 4). Except for group 1 (G1), which received only PBS, the other three groups (G2, G3, and G4) were initially challenged with 10 μg of L. intermedia venom, diluted in 100 μL of NaCl 0.9%, by intradermic injection in the interscapular region. Thirty minutes after the challenge all groups were treated with secretome, except for group 2. Group 1 (G1-control group) received intradermal injection (ID) of 60 μg of secretome in 0.15 M PBS; Group 2 (G2) received 0.9% NaCl via ID; Group 3 (G3) received 60 μg of secretome, via ID and Group 4 (G4), received 60 μg of secretome by intravenous route. Rabbits were evaluated daily and after 15 days were euthanized, necropsied and skin samples around the necrotic lesions were collected for histological analysis.
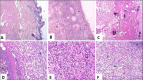
Results: Rabbits of G1 did not present edema, erythema, hemorrhagic halo, or necrosis. In animals from G2, G3, and G4, edema appeared after 6h. However, minor edema was observed in the animals of G2 and G3. Hemorrhagic halo was observed in animals, six hours and three days after, on G2, G3, and G4. Macroscopically, in G4, only one animal out of four had a lesion that evolved into a dermonecrotic wound. No changes were observed in the skin of the animals of G1, by microscopic evaluation. All animals challenged with L. intermedia venom showed similar alterations, such as necrosis and heterophilic infiltration. However, animals from G4 showed fibroblast activation, early development of connective tissue, neovascularization, and tissue re-epithelialization, indicating a more prominent healing process.
Conclusion: These results suggest that secretome from mesenchymal stromal cells cultured in a xeno-free and human component-free culture media can be promising to treat dermonecrosis caused after Loxosceles spiders bite envenoming.
Keywords: Loxosceles intermedia; Loxoscelism; Regenerative therapy; Secretome.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest : The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Malaque CM, Santoro ML, Cardoso JL, Conde MR, Novaes CT, Risk JY, França FO, de Medeiros CR, Fan HW. Clinical picture and laboratorial evaluation in human loxoscelism. Toxicon. 2011;58(8):664–671. - PubMed
-
- remski LH, Trevisan-Silva D, Ferrer VP, Matsubara FH, Meissner GO, Wille AC, Vuitika L, Dias-Lopes C, Ullah A, de Moraes FR, Chávez-Olórtegui C, Barbaro KC, Murakami MT, Arni RK, Senff-Ribeiro A, Chaim OM, Veiga SS. Recent advances in the understanding of brown spider venoms: From the biology of spiders to the molecular mechanisms of toxins. Toxicon. 2014;83:91–120. - PubMed
-
- Pauli I, Minozzo JC, da Silva PH, Chaim OM, Veiga SS. Analysis of therapeutic benefits of antivenin at different time intervals after experimental envenomation in rabbits by venom of the brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia) Toxicon. 2009;53(6):660–671. - PubMed
-
- Maynor ML, Moon RE, Klitzman B, Fracica PJ, Canada A. Brown recluse spider envenomation: a prospective trial of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Acad Emerg Med. 1997;4(3):184–192. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
