Colonic Mucormycosis in Fistulizing Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 39070858
- PMCID: PMC11279494
- DOI: 10.4103/jets.jets_69_23
Colonic Mucormycosis in Fistulizing Crohn's Disease
Abstract
Gastrointestinal mucormycosis, a rare fatal fungal infection in an immunocompromised host, affects mainly the stomach. Colonic mucormycosis is infrequent and is associated with high mortality. Perianal involvement is seen in almost one-third of patients with Crohn's disease. Perianal Crohn's disease is a particularly debilitating form of the disease, which requires multidisciplinary care. It may also require profound immunosuppression with biological agents to control disease activity. Opportunistic infections can complicate the disease course in these patients. We present a case of a middle-aged female with perianal Crohn's disease on adalimumab who developed colonic mucormycosis causing a flare in her disease activity. This patient highlights the need to increase awareness about fungal infections as a cause of disease flare in inflammatory bowel disease.
Keywords: Adalimumab; antitumor necrosis factor α; biological; inflammatory bowel disease.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Emergencies, Trauma, and Shock.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
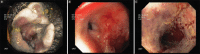
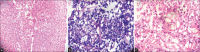
References
-
- Prakash H, Ghosh AK, Rudramurthy SM, Singh P, Xess I, Savio J, et al. A prospective multicenter study on mucormycosis in India: Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Med Mycol. 2019;57:395–402. - PubMed
-
- Goel P, Jain V, Sengar M, Mohta A, Das P, Bansal P. Gastrointestinal mucormycosis: A success story and appraisal of concepts. J Infect Public Health. 2013;6:58–61. - PubMed
-
- Tarrand JJ, Lichterfeld M, Warraich I, Luna M, Han XY, May GS, et al. Diagnosis of invasive septate mold infections. A correlation of microbiological culture and histologic or cytologic examination. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003;119:854–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
