This is a preprint.
Dissecting human monoclonal antibody responses from mRNA- and protein-based XBB.1.5 COVID-19 monovalent vaccines
- PMID: 39071292
- PMCID: PMC11275766
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.07.15.602781
Dissecting human monoclonal antibody responses from mRNA- and protein-based XBB.1.5 COVID-19 monovalent vaccines
Update in
-
Mapping of human monoclonal antibody responses to XBB.1.5 COVID-19 monovalent vaccines: a B cell analysis.Lancet Microbe. 2025 Aug;6(8):101103. doi: 10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101103. Epub 2025 May 30. Lancet Microbe. 2025. PMID: 40456237 Free PMC article.
Abstract
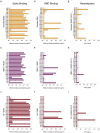
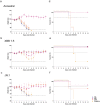
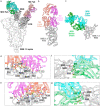
The emergence of highly contagious and immune-evasive severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants has required reformulation of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines to target those new variants specifically. While previous infections and booster vaccinations can enhance variant neutralization, it is unclear whether the monovalent version, administered using either mRNA or protein-based vaccine platforms, can elicit de novo B-cell responses specific for Omicron XBB.1.5 variants. Here, we dissected the genetic antibody repertoire of 603 individual plasmablasts derived from five individuals who received a monovalent XBB.1.5 vaccination either with mRNA (Moderna or Pfizer/BioNtech) or adjuvanted protein (Novavax). From these sequences, we expressed 100 human monoclonal antibodies and determined binding, affinity and protective potential against several SARS-CoV-2 variants, including JN.1. We then select two vaccine-induced XBB.1.5 mAbs, M2 and M39. M2 mAb was a de novo, antibody, i.e., specific for XBB.1.5 but not ancestral SARS-CoV-2. M39 bound and neutralized both XBB.1.5 and JN.1 strains. Our high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of M2 and M39 in complex with the XBB.1.5 spike glycoprotein defined the epitopes engaged and revealed the molecular determinants for the mAbs' specificity. These data show, at the molecular level, that monovalent, variant-specific vaccines can elicit functional antibodies, and shed light on potential functional and genetic differences of mAbs induced by vaccinations with different vaccine platforms.\.
Keywords: Novavax; SARS-CoV-2 mAbs; cryo-EM; mRNA vaccines; monovalent XBB.1.5.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has filed patent applications relating to SARSCoV-2 serological assays, NDV-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines influenza virus vaccines and influenza virus therapeutics which list Florian Krammer as co-inventor. Viviana Simon is listed on the SARS-CoV-2 serological assay patent application as co-inventor. Mount Sinai has spun out a company, Kantaro, to market serological tests for SARS-CoV-2 and another company, CastleVax, to develop SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Florian Krammer is co-founder and scientific advisory board member of CastleVax. Florian Krammer has consulted for Merck, Curevac, GSK, Seqirus and Pfizer and is currently consulting for 3rd Rock Ventures, Gritstone and Avimex. The Krammer laboratory is collaborating with Dynavax on influenza vaccine development and with VIR on influenza virus therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- Zost S. J., Gilchuk P., Case J. B., Binshtein E., Chen R. E., Nkolola J. P., Schäfer A., Reidy J. X., Trivette A., Nargi R. S., Sutton R. E., Suryadevara N., Martinez D. R., Williamson L. E., Chen E. C., Jones T., Day S., Myers L., Hassan A. O., Kafai N. M., Crowe J. E., Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2., Nature 584, 443–449 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cameroni E., Bowen J. E., Rosen L. E., Saliba C., Zepeda S. K., Culap K., Pinto D., VanBlargan L. A., De Marco A., di Iulio J., Zatta F., Kaiser H., Noack J., Farhat N., Czudnochowski N., Havenar-Daughton C., Sprouse K. R., Dillen J. R., Powell A. E., Chen A., Corti D., Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift., Nature 602, 664–670 (2022). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen R. E., Winkler E. S., Case J. B., Aziati I. D., Bricker T. L., Joshi A., Darling T. L., Ying B., Errico J. M., Shrihari S., VanBlargan L. A., Xie X., Gilchuk P., Zost S. J., Droit L., Liu Z., Stumpf S., Wang D., Handley S. A., Stine W. B., Diamond M. S., In vivo monoclonal antibody efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 variant strains., Nature 596, 103–108 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alsoussi W. B., Malladi S. K., Zhou J. Q., Liu Z., Ying B., Kim W., Schmitz A. J., Lei T., Horvath S. C., Sturtz A. J., McIntire K. M., Evavold B., Han F., Scheaffer S. M., Fox I. F., Mirza S. F., Parra-Rodriguez L., Nachbagauer R., Nestorova B., Chalkias S., Ellebedy A. H., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron boosting induces de novo B cell response in humans., Nature 617, 592–598 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
