Integrative analysis of Anoikis-related genes reveals that FASN is a novel prognostic biomarker and promotes the malignancy of bladder cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 39071712
- PMCID: PMC11283158
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34029
Integrative analysis of Anoikis-related genes reveals that FASN is a novel prognostic biomarker and promotes the malignancy of bladder cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
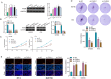
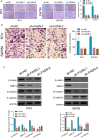
Bladder cancer (BC) exhibits diversity in clinical outcomes and is characterized by heterogeneity. Anoikis, a form of programmed cell death, plays a crucial role in facilitating tumor invasion and metastasis. This study comprehensively investigated the genetic landscape of BC progression, identifying 300 differentially expressed Anoikis-related genes (DE-ARGs) through in-depth analysis of the GSE13507 datasets. Functional enrichment analysis revealed associations with diverse diseases and biological processes. Employing machine learning algorithms, a logistic regression model based on nine marker genes demonstrated superior accuracy in distinguishing BC from normal samples. Validation in TCGA datasets highlighted the prognostic significance of LRP1, FASN, and SIRT6, suggesting their potential as cancer biomarkers. Particularly, FASN emerged as an independent prognostic indicator, regulating BC cell proliferation and metastasis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. The study provides crucial insights into altered genetic landscapes and potential therapeutic strategies for BC, emphasizing the significance of FASN in BC prognosis and progression.
Keywords: Anoikis-related genes; Biomarker; Bladder cancer; FASN; Machine learning; Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of mitochondria-related genes indicates that PPP2R2B is a novel biomarker and promotes the progression of bladder cancer via Wnt signaling pathway.Biol Direct. 2024 Feb 26;19(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00461-6. Biol Direct. 2024. PMID: 38409085 Free PMC article.
-
A novel anoikis-related gene signature identifies LYPD1 as a novel therapy target for bladder cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 8;14(1):3198. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53272-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38332160 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of multi-omic prognostic signature of anoikis-related genes in liver hepatocellular carcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 17;102(46):e36190. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036190. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37986299 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative transcriptional characterization of cell cycle checkpoint genes promotes clinical management and precision medicine in bladder carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 11;12:915662. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.915662. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36033441 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the significance of anoikis in bladder cancer and systematic analysis of S100A7 as a potential therapeutic target.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 12;29(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01642-9. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38217031 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metabolic reprogramming and signaling adaptations in anoikis resistance: mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun;480(6):3315-3342. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05199-3. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39821582 Review.
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Wagle N.S., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2023;73(1):17–48. - PubMed
-
- Jubber I., Ong S., Bukavina L., Black P.C., Compérat E., Kamat A.M., et al. Epidemiology of bladder cancer in 2023: a systematic review of risk factors. Eur. Urol. 2023;84(2):176–190. - PubMed
-
- Lenis A.T., Lec P.M., Chamie K., Mshs M.D. Bladder cancer: a review. JAMA. 2020;324(19):1980–1991. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

