Phase separation is regulated by post-translational modifications and participates in the developments of human diseases
- PMID: 39071719
- PMCID: PMC11279762
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34035
Phase separation is regulated by post-translational modifications and participates in the developments of human diseases
Abstract
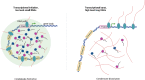
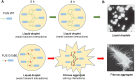
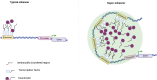
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) of intracellular proteins has emerged as a hot research topic in recent years. Membrane-less and liquid-like condensates provide dense spaces that ensure cells to high efficiently regulate genes transcription and rapidly respond to burst changes from the environment. The fomation and activity of LLPS are not only modulated by the cytosol conditions including but not limited to salt concentration and temperture. Interestingly, recent studies have shown that phase separation is also regulated by various post-translational modifications (PTMs) through modulating proteins multivalency, such as solubility and charge interactions. The regulation mechanism is crucial for normal functioning of cells, as aberrant protein aggregates are often closely related with the occurrence and development of human diseases including cancer and nurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, studying phase separation in the perspective of protein PTMs has long-term significance for human health. In this review, we summarized the properties and cellular physiological functions of LLPS, particularly its relationships with PTMs in human diseases according to recent researches.
Keywords: Cancer; Condensates; Phase separation; Protein interactions; Protein post-translational modifications.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Friend or foe-Post-translational modifications as regulators of phase separation and RNP granule dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 3;294(18):7137-7150. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.001189. Epub 2018 Dec 26. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30587571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-translational modifications in liquid-liquid phase separation: a comprehensive review.Mol Biomed. 2022 May 11;3(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s43556-022-00075-2. Mol Biomed. 2022. PMID: 35543798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of liquid-liquid phase separation with focus on post-translational modifications.Chem Commun (Camb). 2021 Dec 9;57(98):13275-13287. doi: 10.1039/d1cc05266g. Chem Commun (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34816836 Review.
-
[Latest Findings on Phase Separation of Cytomechanical Proteins].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jan 20;55(1):19-23. doi: 10.12182/20240160206. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38322526 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Liquid-liquid phase separation as triggering factor of fibril formation.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2024;206:143-182. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2024.03.006. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38811080 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the dynamic drivers: phase separation's pivotal role in stem cell biology and therapeutic potential.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 May 30;16(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04403-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40442783 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brangwynne C.P., et al. Germline P granules are liquid droplets that localize by controlled dissolution/condensation. Science. 2009;324(5935):1729–1732. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

