The Danish Ibbis Trials for Sickness Absentees with Common Mental Disorders: A Phase 4 Prospective Study Comparing Randomized Trial and Real-World Data
- PMID: 39071746
- PMCID: PMC11276403
- DOI: 10.5334/ijic.7562
The Danish Ibbis Trials for Sickness Absentees with Common Mental Disorders: A Phase 4 Prospective Study Comparing Randomized Trial and Real-World Data
Abstract
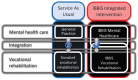
Introduction: In two randomized controlled trials (RCT) we tested the efficacy of a novel integrated vocational rehabilitation and mental healthcare intervention, coined INT, for sickness absentees with common mental disorders. The aim was to improve vocational outcomes compared to Service As Usual (SAU). Contrary to expectations, the delivered intervention caused worse outcomes within some diagnostic groups and some benefits in others. In this phase 4 study, we examined the effectiveness of the intervention in real-world practice.
Method: In this prospective intervention study, we allocated adult sickness absentees with either depression, anxiety, or adjustment disorder to receive INT in a real-world setting in a Danish Municipality. We compared the vocational outcomes of this group to a matched group who received INT as a part of the RCTs, after randomization to the intervention group herein. Primary outcome was return to work at any point within 12 months.
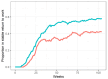
Results: In the real-world group, 151 participants received INT during 2019. From the randomized trials, 302 matched participants who received INT between 2016-2018 were included. On the primary outcome - return to work within 12 months - the real-word group fared worse (48.3 vs 64.6 %, OR 0.54 [95%CI: 0.37-0.79], p = 0.001). Across most other vocational outcomes, a similar pattern of statistically significant poorer outcomes in the real-world group was observed: Lower number of weeks in work and lower proportion in work at 12 months (42.3% vs. 58.3% (p = 0.002)).
Discussion: The real-word group showed significantly worse vocational outcomes. Like in many other studies of complex interventions, implementation was difficult in the original randomized trials and perhaps even more difficult in the less structured real-world setting. Since the intervention was less effective for some groups compared to SAU in the original trial, this negative effect may be even more pronounced in a real-world setting.
Keywords: anxiety; common mental disorders; depression; integrated care; vocational rehabilitation.
Copyright: © 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Mikkelsen MB, Rosholm M. Systematic review and meta-analysis of interventions aimed at enhancing return to work for sick-listed workers with common mental disorders, stress-related disorders, somatoform disorders and personality disorders. Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2018. DOI: 10.1136/oemed-2018-105073 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials