Piloting a scale-up platform for high-quality human T-cells production
- PMID: 39071806
- PMCID: PMC11282488
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1427171
Piloting a scale-up platform for high-quality human T-cells production
Abstract
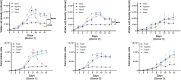
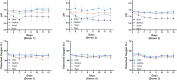
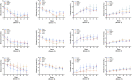
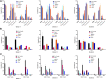
Cell and gene therapies are an innovative solution to various severe diseases and unfulfilled needs. Adoptive cell therapy (ACT), a form of cellular immunotherapies, has been favored in recent years due to the approval of chimeric antigen receptor CAR-T products. Market research indicates that the industry's value is predicted to reach USD 24.4 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.5%. More importantly, ACT is recognized as the hope and future of effective, personalized cancer treatment for healthcare practitioners and patients worldwide. The significant global momentum of this therapeutic approach underscores the urgent need to establish it as a practical and standardized method. It is essential to understand how cell culture conditions affect the expansion and differentiation of T-cells. However, there are ongoing challenges in ensuring the robustness and reproducibility of the manufacturing process. The current study evaluated various adoptive T-cell culture platforms to achieve large-scale production of several billion cells and high-quality cellular output with minimal cell death. It examined factors such as bioreactor parameters, media, supplements and stimulation. This research addresses the fundamental challenges of scalability and reproducibility in manufacturing, which are essential for making adoptive T-cell therapy an accessible and powerful new class of cancer therapeutics.
Keywords: T-cell; adoptive cell therapy; biaxial rotary bioreactor; bioprocessing; scale-up; stirred-tank bioreactor.
Copyright © 2024 Selvarajan, Teo, Chang, Ng, Cheong, Sivalingam, Khoo, Wong and Loo.
Conflict of interest statement
Author NC was employed by Quintech Life Sciences Pte. Ltd. Authors JS and GK were employed by Tessa Therapeutics Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

