Osteopontin: A novel marker of pre-symptomatic sporadic Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39072932
- PMCID: PMC11497655
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14065
Osteopontin: A novel marker of pre-symptomatic sporadic Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: We investigate the role of osteopontin (OPN) in participants with Pre-symptomatic Alzheimer's disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and in AD brains.
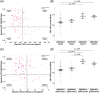
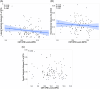
Methods: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) OPN, AD, and synaptic biomarker levels were measured in 109 cognitively unimpaired (CU), parental-history positive Pre-symptomatic Evaluation of Experimental or Novel Treatments for Alzheimer's Disease (PREVENT-AD) participants, and in 167 CU and 399 participants with MCI from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) cohort. OPN levels were examined as a function of amyloid beta (Aβ) and tau positivity. Survival analyses investigated the link between OPN and rate of conversion to AD.
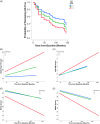
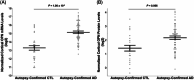
Results: In PREVENT-AD, CSF OPN was positively correlated with synaptic biomarkers. In PREVENT-AD and ADNI, OPN was elevated in CSF Aβ42/40(+)/total tau(+) and CSF Aβ42/40(+)/phosphorylated tau181(+) individuals. In ADNI, OPN was increased in Aβ(+) positron emission tomography (PET) and tau(+) PET individuals, and associated with an accelerated rate of conversion to AD. OPN was elevated in autopsy-confirmed AD brains.
Discussion: Strong associations between CSF OPN and key markers of AD pathophysiology suggest a significant role for OPN in tau neurobiology, particularly in the early stages of the disease.
Highlights: In the Pre-symptomatic Evaluation of Experimental or Novel Treatments for Alzheimer's Disease cohort, we discovered that cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) osteopontin (OPN) levels can indicate early synaptic dysfunction, tau deposition, and neuronal loss in cognitively unimpaired elderly with a parental history. CSF OPN is elevated in amyloid beta(+) positron emission tomography (PET) and tau(+) PET individuals. Elevated CSF OPN is associated with an accelerated rate of conversion to Alzheimer's disease (AD). Elevated CSF OPN is associated with an accelerated rate of cognitive decline on the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive subscale 13, Montreal Cognitive Assessment, Mini-Mental State Examination, and Clinical Dementia Rating Scale Sum of Boxes. OPN mRNA and protein levels are significantly upregulated in the frontal cortex of autopsy-confirmed AD brains.
Keywords: post mortem; Alzheimer's disease; Pre‐symptomatic; autopsied brains; biomarkers; cerebral ventricles; cerebrospinal fluid; mRNA; neuroinflammation; osteopontin; positron emission tomography; secreted phosphoprotein 1; synaptic markers.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
JP serves as a scientific advisor to the Alzheimer Society of France. HZ has served on scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave; has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). KB has served as a consultant and on advisory boards for Acumen, ALZPath, BioArctic, Biogen, Eisai, Lilly, Moleac Pte. Ltd, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers; has served on data monitoring committees for Julius Clinical and Novartis; has given lectures, produced educational materials, and participated in educational programs for AC Immune, Biogen, Celdara Medical, Eisai, and Roche Diagnostics; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program, outside the work presented in this paper. MJQ, AL, CP, DCB, AB, and SV have nothing to disclose. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Canada Foundation for Innovation
- #AF-939721/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- #2022-01018/Swedish Research Council
- Olav Thon Foundation
- #ALFGBG-715986/ALF1052 agreement
- #2019-02397/Swedish Research Council
- U01 AG024904/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- JPND2019-466-236/European Union Joint Program for Neurodegenerative Disorders
- EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé (FRQS)
- Stiftelsen för Gamla Tjänarinnor
- W81XWH-12-2-0012/DOD ADNI
- #2022-00732/Swedish Research Council
- National Institute for Health and Care Research University College London Hospitals Biomedical Research Centre
- 860197/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- ZEN-21-848495/Alzheimer's Association 2021 Zenith Award
- #ADSF-21-831381-C/AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- #FO2017-0243/Hjärnfonden, Sweden
- #AF-930351/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- #ALZ2022-0006/Hjärnfonden, Sweden
- #ALFGBG-965240/ALF1052 agreement
- SG-23-1038904QC/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- #2017-00915/Swedish Research Council
- #201809-2016862/Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation
- #PJT 153287/CIHR/Canada
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Swedish government and the County Councils
- JPND2021-00694/European Union Joint Programme-Neurodegenerative Disease Research
- Erling-Persson Family Foundation
- Brain Canada Foundation
- Bluefield Project
- McGill University
- #ADSF-21-831377-C/AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- #ADSF-21-831376-C/AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- #FO2022-0270/Hjärnfonden, Sweden
- #AF-968270/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- #ALFGBG-71320/Swedish State Support for Clinical Research
- Levesque Foundation
- UKDRI-1003/UK Dementia Research Institute
- 101053962/European Union's Horizon Europe research and innovation programme
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

