Galectin 3-binding protein (LGALS3BP) depletion attenuates hepatic fibrosis by reducing transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) availability and inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 39073023
- PMCID: PMC11483554
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12600
Galectin 3-binding protein (LGALS3BP) depletion attenuates hepatic fibrosis by reducing transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) availability and inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
Background: Increased Galectin 3-binding protein (LGALS3BP) serum levels have been used to assess hepatic fibrosis stages and the severity of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Considering the crucial role of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) in the emergence of these diseases, the present study tested the hypothesis that LGALS3BP regulates the TGF-β1 signaling pathway.
Methods: The expression levels of LGALS3BP and TGFB1 were analyzed in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) and HCC. Multiple omics techniques, such as RNA-sequencing, transposase-accessible chromatin-sequencing assay, and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry proteomics, were used to identify the regulatory mechanisms for the LGALS3BP-TGF-β1 axis. The effects of altered TGF-β1 signaling by LGALS3BP were investigated in conditional LGALS3BP-knockin and LGALS3BP-knockout mice.
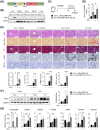
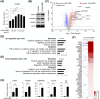
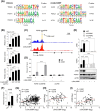
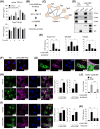
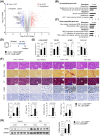
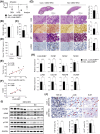
Results: In patients with MASH and HCC, the levels of LGALS3BP and TGFB1 exhibited positive correlations. Stimulation of LGALS3BP by the inflammatory cytokine interferon α in HCC cells or ectopic overexpression of LGALS3BP in hepatocytes promoted the expression levels of TGFB1. Aggravated fibrosis was observed in the livers of hepatocyte-specific LGALS3BP-knockin mice, with increased TGFB1 levels. LGALS3BP directly bound to and assembled integrin αV, an integral mediator required for releasing active TGF-β1 from extracellular latent complex with the rearranged F-actin cytoskeleton. The released TGF-β1 activated JunB transcription factor, which in turn promoted the TGF-β1 positive feedback loop. LGALS3BP deletion in the hepatocytes downregulated TGF-β1 signaling and CCl4 induced fibrosis. Moreover, LGALS3BP depletion hindered hepatocarcinogenesis by limiting the availability of fibrogenic TGF-β1.
Conclusion: LGALS3BP plays a crucial role in hepatic fibrosis and carcinogenesis by controlling the TGF-β1 signaling pathway, making it a promising therapeutic target in TGF-β1-related diseases.
Keywords: FAK; F‐actin; Integrin αV; Interferon α; JunB; LGALS3BP; TGF‐β1; hepatic carcinogenesis; metabolic dysfuntion‐associated steatohepatitis; tensile force.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Sun Yat‐sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):6. - PubMed
-
- Ringelhan M, Pfister D, O'Connor T, Pikarsky E, Heikenwalder M. The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Immunol. 2018;19(3):222–232. - PubMed
-
- Craig AJ, von Felden J, Garcia‐Lezana T, Sarcognato S, Villanueva A. Tumour evolution in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17(3):139–152. - PubMed
-
- Loimaranta V, Hepojoki J, Laaksoaho O, Pulliainen AT. Galectin‐3‐binding protein: A multitask glycoprotein with innate immunity functions in viral and bacterial infections. J Leukoc Biol. 2018;104(4):777–786. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

