Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases the effect of 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy on experimental colorectal cancer in mice
- PMID: 39073340
- PMCID: PMC466994
- DOI: 10.4103/2045-9912.385944
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases the effect of 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy on experimental colorectal cancer in mice
Abstract
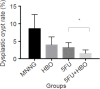
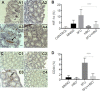
Tumor hypoxia may compromise the results of chemotherapy for treating colorectal cancer because it stimulates angiogenesis and the release of tumor growth factors. Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) supplementation may potentiate the effects of chemotherapy in such cases. This study aimed to assess the effect of HBO therapy combined with chemotherapy on the treatment of colorectal cancer in mice. C57BL6 mice were submitted to the intrarectal instillation of N-methyl-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) and treated with 5-fluorouracil (5FU) and/or HBO therapy. The MNNG group presented the highest dysplastic crypt rate. The 5FU + HBO group presented the highest rate of apoptotic cells per dysplastic crypt. The 5FU group presented the highest expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and CD44. HBO therapy increased the effect of 5FU on the treatment of the experimental colorectal neoplasia in mice.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Medical Gas Research.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Incidência de Câncer no Brasil. Instituto Nacional de Saúde da Mulher, da Criança e do Adolescente Fernandes Figueira (IFF/Fiocruz) Estimativa. 2018. https://portaldeboasprati-cas.iff.fiocruz.br/biblioteca/estimativa-2018-... . Accessed April 28, 2022.
-
- Seow-En I, Chen WT. Complete mesocolic excision with central venous ligation/D3 lymphadenectomy for colon cancer - A comprehensive review of the evidence. Surg Oncol. 2022;42:101755. - PubMed
-
- Steele SR, Hull TL, Read TE, Saclarides TJ, Senagore AJ, Whitlow CB. The ASCRS Textbook of Colon and Rectal Surgery. Cham: Springer; 2016.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

