Timing matters in the use of renin-angiotensin system modulators and COVID-related cognitive and cerebrovascular dysfunction
- PMID: 39074114
- PMCID: PMC11285960
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304135
Timing matters in the use of renin-angiotensin system modulators and COVID-related cognitive and cerebrovascular dysfunction
Abstract
Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) modulators, including Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI), are effective medications for controlling blood pressure. Cognitive deficits, including lack of concentration, memory loss, and confusion, were reported after COVID-19 infection. ARBs or ACEI increase the expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2), a functional receptor that allows binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein for cellular invasion. To date, the association between the use of RAS modulators and the severity of COVID-19 cognitive dysfunction is still controversial.
Purpose: This study addressed the following questions: 1) Does prior treatment with RAS modulator worsen COVID-19-induced cerebrovascular and cognitive dysfunction? 2) Can post-treatment with RAS modulator improve cognitive performance and cerebrovascular function following COVID-19? We hypothesize that pre-treatment exacerbates COVID-19-induced detrimental effects while post-treatment displays protective effects.
Methods: Clinical study: Patients diagnosed with COVID-19 between May 2020 and December 2022 were identified through the electronic medical record system. Inclusion criteria comprised a documented medical history of hypertension treated with at least one antihypertensive medication. Subsequently, patients were categorized into two groups: those who had been prescribed ACEIs or ARBs before admission and those who had not received such treatment before admission. Each patient was evaluated on admission for signs of neurologic dysfunction. Pre-clinical study: Humanized ACE-2 transgenic knock-in mice received the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein via jugular vein injection for 2 weeks. One group had received Losartan (10 mg/kg), an ARB, in their drinking water for two weeks before the injection, while the other group began Losartan treatment after the spike protein injection. Cognitive functions, cerebral blood flow, and cerebrovascular density were determined in all experimental groups. Moreover, vascular inflammation and cell death were assessed.
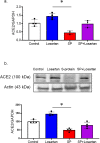
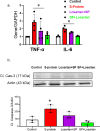
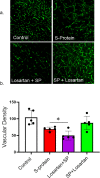
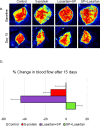
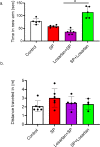
Results: Signs of neurological dysfunction were observed in 97 out of 177 patients (51%) taking ACEIs/ARBs prior to admission, compared to 32 out of 118 patients (27%) not receiving ACEI or ARBs. In animal studies, spike protein injection increased vascular inflammation, increased endothelial cell apoptosis, and reduced cerebrovascular density. In parallel, spike protein decreased cerebral blood flow and cognitive function. Our results showed that pretreatment with Losartan exacerbated these effects. However, post-treatment with Losartan prevented spike protein-induced vascular and neurological dysfunctions.
Conclusion: Our clinical data showed that the use of RAS modulators before encountering COVID-19 can initially exacerbate vascular and neurological dysfunctions. Similar findings were demonstrated in the in-vivo experiments; however, the protective effects of targeting the RAS become apparent in the animal model when the treatment is initiated after spike protein injection.
Copyright: © 2024 Meier et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
Some data were presented as an abstract at the International Stroke Conference 2023 and the MIDYEAR 2023 Clinical Meeting & Exhibition. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. Funding:This study was supported by American Heart Association 23AIREA1045073 to MA.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

