Rabenosyn-5 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer metastasis via inhibiting CDC42 activity
- PMID: 39075137
- PMCID: PMC11489121
- DOI: 10.1038/s41417-024-00813-4
Rabenosyn-5 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer metastasis via inhibiting CDC42 activity
Abstract
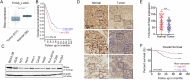
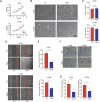
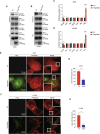
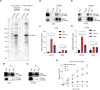
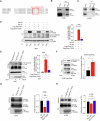
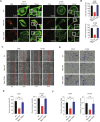
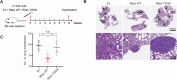
Metastasis, the primary cause of death in lung cancer patients, is facilitated by cytoskeleton remodeling, which plays a crucial role in cancer cell migration and invasion. However, the precise regulatory mechanisms of intracellular trafficking proteins involved in cytoskeleton remodeling remain unclear. In this study, we have identified Rabenosyn-5 (Rbsn) as an inhibitor of filopodia formation and lung cancer metastasis. Mechanistically, Rbsn interacts with CDC42 and functions as a GTPase activating protein (GAP), thereby inhibiting CDC42 activity and subsequent filopodia formation. Furthermore, we have discovered that Akt phosphorylates Rbsn at the Thr253 site, and this phosphorylation negates the inhibitory effect of Rbsn on CDC42 activity. Additionally, our analysis reveals that Rbsn expression is significantly downregulated in lung cancer, and this decrease is associated with a worse prognosis. These findings provide strong evidence supporting the role of Rbsn in suppressing lung cancer progression through the inhibition of metastasis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Goldstraw P, Ball D, Jett JR, Le Chevalier T, Lim E, Nicholson AG, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 2011;378:1727–40. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL, et al. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 2017;389:299–311. - PubMed
-
- Relli V, Trerotola M, Guerra E, Alberti S. Abandoning the notion of non-small cell lung cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25:585–94. - PubMed
-
- Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K, Novello S, Smit EF, Faivre-Finn C, et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:iv192–iv237. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- LJKM20221787/Foundation of Liaoning Province Education Administration (Liaoning Province Education Administration Foundation)
- 2022JJ30364/Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department (Department of Science and Technology of Hunan Province)
- 2020-MS-309/Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation)
- 2022-NLTS-14-04/Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

