Tracking EEG network dynamics through transitions between eyes-closed, eyes-open, and task states
- PMID: 39075178
- PMCID: PMC11286934
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68532-2
Tracking EEG network dynamics through transitions between eyes-closed, eyes-open, and task states
Abstract
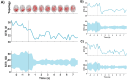
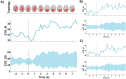
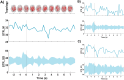
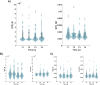
Our study aimed to verify the possibilities of effectively applying chronnectomics methods to reconstruct the dynamic processes of network transition between three types of brain states, namely, eyes-closed rest, eyes-open rest, and a task state. The study involved dense EEG recordings and reconstruction of the source-level time-courses of the signals. Functional connectivity was measured using the phase lag index, and dynamic analyses concerned coupling strength and variability in alpha and beta frequencies. The results showed significant and dynamically specific transitions regarding processes of eyes opening and closing and during the eyes-closed-to-task transition in the alpha band. These observations considered a global dimension, default mode network, and central executive network. The decrease of connectivity strength and variability that accompanied eye-opening was a faster process than the synchronization increase during eye-opening, suggesting that these two transitions exhibit different reorganization times. While referring the obtained results to network studies, it was indicated that the scope of potential similarities and differences between rest and task-related networks depends on whether the resting state was recorded in eyes closed or open condition.
Keywords: Chronnectomics; Default mode network; EEG; Functional connectivity; Neural networks.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
EEG Signatures of Dynamic Functional Network Connectivity States.Brain Topogr. 2018 Jan;31(1):101-116. doi: 10.1007/s10548-017-0546-2. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Brain Topogr. 2018. PMID: 28229308 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the alpha desynchronization hypothesis in resting state networks with intracranial electroencephalography and wiring cost estimates.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 15;7(1):15670. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15659-0. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29142213 Free PMC article.
-
Brain state dynamics differ between eyes open and eyes closed rest.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Jul 15;45(10):e26746. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26746. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38989618 Free PMC article.
-
Opening or closing eyes at rest modulates the functional connectivity of V1 with default and salience networks.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 4;10(1):9137. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66100-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32499585 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamical balance of the brain at rest.Neuroscientist. 2011 Feb;17(1):107-23. doi: 10.1177/1073858409354384. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Neuroscientist. 2011. PMID: 21196530 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neural transmission in the wired brain, new insights into an encoding-decoding-based neuronal communication model.Transl Psychiatry. 2025 Aug 16;15(1):288. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03506-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40819087 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

