Cardiac-gated spectroscopic photoacoustic imaging for ablation-induced necrotic lesion visualization
- PMID: 39075610
- PMCID: PMC12186712
- DOI: 10.1002/jbio.202400126
Cardiac-gated spectroscopic photoacoustic imaging for ablation-induced necrotic lesion visualization
Abstract
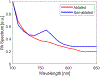
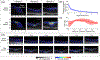
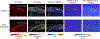
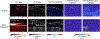
Radiofrequency (RF) ablation is a minimally invasive therapy for atrial fibrillation. Conventional RF procedures lack intraoperative monitoring of ablation-induced necrosis, complicating assessment of completeness. While spectroscopic photoacoustic (sPA) imaging shows promise in distinguishing ablated tissue, multi-spectral imaging is challenging in vivo due to low imaging quality caused by motion. Here, we introduce a cardiac-gated sPA imaging (CG-sPA) framework to enhance image quality using a motion-gated averaging filter, relying on image similarity. Necrotic extent was calculated based on the ratio between spectral unmixed ablated tissue contrast and total tissue contrast, visualizing as a continuous color map to highlight necrotic area. The validation of the concept was conducted in both ex vivo and in vivo swine models. The ablation-induced necrotic lesion was successfully detected throughout the cardiac cycle through CG-sPA imaging. The results suggest the CG-sPA imaging framework has great potential to be incorporated into clinical workflow to guide ablation procedures intraoperatively.
Keywords: cardiac ablation; cardiac gating; image‐guided intervention; in vivo demonstration; spectroscopic photoacoustic imaging.
© 2024 Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
Tommaso Mansi was a scientist and employee of Siemens Healthineers USA during this work and currently is a scientist and employee of Janssen: Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson. Young-Ho Kim and Florin-Cristian Ghesu are scientists and employees of Siemens Healthineers USA. The other authors have stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article.
Figures







References
-
- “Atrial Fibrillation | cdc.gov,” https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/atrial_fibrillation.htm.
-
- Peters DC, Wylie JV, Hauser TH, Nezafat R, Han Y, Woo JJ, Taclas J, Kissinger KV, Goddu B, Josephson ME, and Manning WJ, “Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation Correlates With the Extent of Post-Procedural Late Gadolinium Enhancement. A Pilot Study,” JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2(3), 308–316 (2009). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

