Effects of FGF2 Priming and Nrf2 Activation on the Antioxidant Activity of Several Human Dental Pulp Cell Clones Derived From Distinct Donors, and Therapeutic Effects of Transplantation on Rodents With Spinal Cord Injury
- PMID: 39076100
- PMCID: PMC11289817
- DOI: 10.1177/09636897241264979
Effects of FGF2 Priming and Nrf2 Activation on the Antioxidant Activity of Several Human Dental Pulp Cell Clones Derived From Distinct Donors, and Therapeutic Effects of Transplantation on Rodents With Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
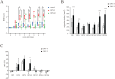
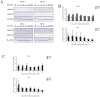
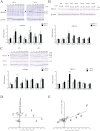
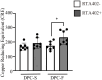
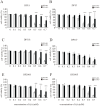
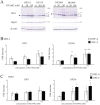
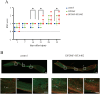
In recent years, the interest in cell transplantation therapy using human dental pulp cells (DPCs) has been increasing. However, significant differences exist in the individual cellular characteristics of human DPC clones and in their therapeutic efficacy in rodent models of spinal cord injury (SCI); moreover, the cellular properties associated with their therapeutic efficacy for SCI remain unclear. Here, using DPC clones from seven different donors, we found that most of the clones were highly resistant to H2O2 cytotoxicity if, after transplantation, they significantly improved the locomotor function of rats with complete SCI. Therefore, we examined the effects of the basic fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) and bardoxolone methyl (RTA402), which is a nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) chemical activator, on the total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and the resistance to H2O2 cytotoxicity. FGF2 treatment enhanced the resistance of a subset of clones to H2O2 cytotoxicity. Regardless of FGF2 priming, RTA402 markedly enhanced the resistance of many DPC clones to H2O2 cytotoxicity, concomitant with the upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NAD(P)H-quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1). With the exception of a subset of clones, the TAC was not increased by either FGF2 priming or RTA402 treatment alone, whereas it was significantly upregulated by both treatments in each clone, or among all seven DPC clones together. Thus, the TAC and resistance to H2O2 cytotoxicity were, to some extent, independently regulated and were strongly enhanced by both FGF2 priming and RTA402 treatment. Moreover, even a DPC clone that originally exhibited no therapeutic effect on SCI improved the locomotor function of mice with SCI after transplantation under both treatment regimens. Thus, combined with FGF2, RTA402 may increase the number of transplanted DPCs that migrate into and secrete neurotrophic factors at the lesion epicenter, where reactive oxygen species are produced at a high level.
Keywords: antioxidant factors; clonal difference; human dental pulp cells; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) chemical activator (RTA402); spinal cord injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Shingu H, Ohama M, Ikata T, Katoh S, Akatsu T. A nationwide epidemiological survey of spinal cord injuries in Japan from January 1990 to December 1992. Paraplegia. 1995;33(4):183–88. - PubMed
-
- Miyakoshi N, Suda K, Kudo D, Sakai H, Nakagawa Y, Mikami Y, Suzuki S, Tokioka T, Tokuhiro A, Takei H, Katoh S, et al. A nationwide survey on the incidence and characteristics of traumatic spinal cord injury in Japan in 2018. Spinal Cord. 2021;59(6):626–34. - PubMed
-
- Tsuji O, Sugai K, Yamaguchi R, Tashiro S, Nagoshi N, Kohyama J, Iida T, Ohkubo T, Itakura G, Isoda M, Shinozaki M, et al. Concise review: laying the groundwork for a first-in-human study of an induced pluripotent stem cell-based intervention for spinal cord injury. Stem Cells. 2019;37(1):6–13. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kong H, Liu P, Li H, Zeng X, Xu P, Yao X, Liu S, Cheng CK, Xu J. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: the novel therapeutic option for regenerative dentistry. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(1):46–58. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

